Classwork 3
Co-Intelligence Rule Practice
Rule 1: Always Invite AI to the Table
Ask an AI tool to generate three possible titles for a student newsletter about “AI and College Life” (covering study tips, career opportunities, and ethical concerns).
As a group, compare the three titles and choose the best.
Discussion Questions:
1. Which title is the most engaging and memorable?
2. Which one best captures the range of topics?
3. How would you combine or tweak the titles to make an even better one?
Rule 2: Be the Human in the Loop (HITL)
Consider this fabricated AI claim:
“AI-generated code is always more efficient and less buggy than code written by humans.”
Task: Work in pairs or groups to identify what’s misleading or incorrect about this claim.
Discussion Questions:
1. What makes this statement inaccurate or overstated?
2. How could relying on AI code without oversight create real risks?
3. What steps (fact-checking, testing, cross-checking) should you take before trusting AI outputs?
Rule 3: Treat AI Like a Person (but Remember It Isn’t)
Use the persona-prompt template below:
You are a [role] helping [audience].
Constraints: [tone, length, format].
Task: [deliverable].
Criteria: [rubric].Rewrite this prompt to make it more specific and effective for a sample task (e.g., “Describe climate change”).
- Define the role (e.g., teacher, journalist, scientist).
- Clarify the audience (e.g., middle school students, undergraduate students, policymakers).
- Add useful constraints (tone, word limit, style).
- Refine the task and criteria so the output is clear and useful.
See also
Check out OpenAI’s “100 Chats for College Students” — a student-made guide to learning strategies, study habits, career exploration, wellness, and day-to-day problem-solving.
Rule 4: Assume This Is the Worst AI You’ll Ever Use
AI tools are improving at a rapid pace. Imagine that today’s systems are the least powerful you’ll ever work with.
👉 If that’s true, what skills should you focus on developing now so you can stay valuable and adaptable as AI keeps getting better?
Discussion Questions:
1. Which skills do humans bring that AI can’t easily replace?
2. How can you prepare for a world where AI does many technical tasks better than people?
3. In what ways can you treat today’s AI as a “prototype” to practice for tomorrow’s tools?
Sample Essay
AI tools are improving fast. If today’s systems are the least powerful you’ll ever use, your goal in college isn’t just to use AI—it’s to grow with it. Three ideas to guide you:
- Generative AI is a predicting-and-remixing machine (it guesses likely words, code, or steps from patterns).
- Because AI is confident but not always correct, your understanding and verification matter more, not less.
- Your edge is human: domain knowledge, creativity, and judgment (context, ethics, teamwork).
Two perspectives shape this essay:
- BCG Henderson Institute (“GenAI Doesn’t Just Increase Productivity. It Expands Capabilities.”) finds that GenAI can immediately expand what non-experts can do, yet it doesn’t automatically help them learn the underlying skills. The gap between “doing with AI” and “knowing how to do it yourself” is where your long-term value is built.
- Simo (“Expanding economic opportunity with AI.”) argues that AI can unlock opportunity at scale (new roles, better matches between workers and employers), but only if people become AI-fluent and organizations build clear pathways (jobs platforms, practical certifications, and training aligned to real employer needs).
Framing: When and how to pair humans with GenAI
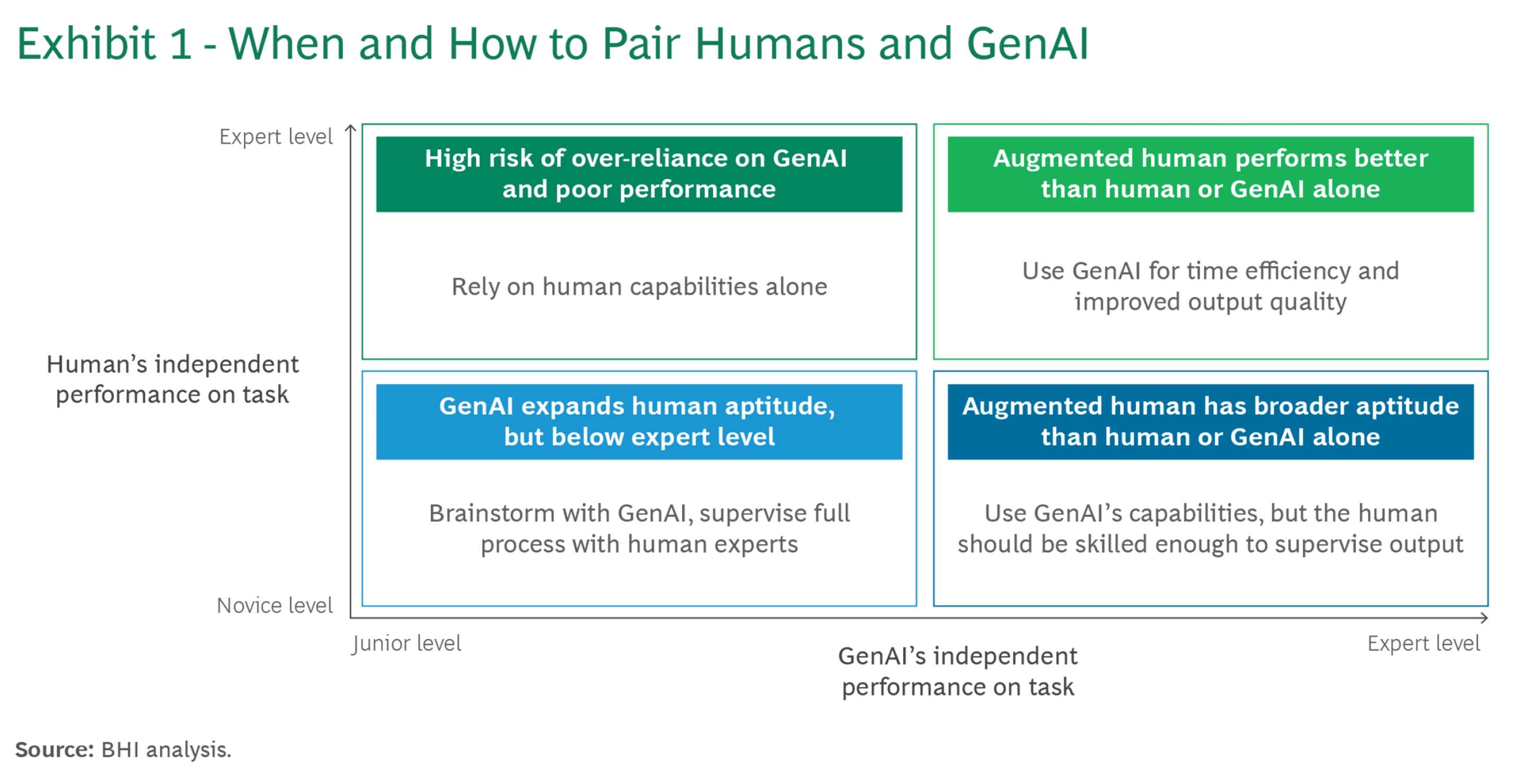
Up/down = how strong the human is on a task. Left/right = how strong the AI is on that task.
What it means for you.
- Top-right (use AI confidently): You + AI are strong → you go faster and keep quality high (great for drafting, refactoring, and summarizing work you already understand).
- Top-left (don’t over-rely): You’re strong, AI is weak → trust your own method; use AI for small ideas, not final answers.
- Bottom-right (supervise + learn): AI is strong, you’re new → AI can expand your capabilities today, but you must check its work and learn the basics.
- Bottom-left (learn first): Neither is strong → start with a mini-lesson, example, or office hours before delegating to AI.
As access to AI tools grows—through free versions, student-friendly platforms, and training programs offered by schools or employers—more students will find themselves in the bottom-right quadrant of the human–AI map. In this position, the AI is strong at a task, while the human is still developing skills. This means AI can help you perform at a higher level earlier than you could on your own, letting you complete assignments, projects, or coding tasks that might otherwise feel out of reach. But this shortcut also comes with a trap: you might lean too heavily on AI without actually understanding what’s happening.
Your responsibility is to move up the human-skill axis, which means turning AI-assisted performance into genuine knowledge and ability. That requires doing the hard work of learning—checking outputs manually, practicing problem-solving without AI, and reflecting on why a solution works. In other words, use AI as a springboard to support your growth, while also making sure you understand the underlying concepts yourself. The real value comes from combining AI-assisted performance with your own learning. As you continue to practice and reflect, you’ll gradually build the kind of durable expertise that helps on exams, in internships, and later in your career.
1) Which human skills are hardest for AI to replace?
AI can sound right while being wrong. That is why your role is not to accept outputs at face value but to notice missing assumptions, wrong units, shaky causal stories, and conclusions that don’t fit the real-world context. The best way to build this filter is to deepen yourself in at least one domain this semester—data analytics, economics, finance, marketing, accounting, or another field you care about. As your domain knowledge grows, your prompts get sharper, your checks get stronger, and your conversations with AI become more productive.
Humans also excel at problem-finding and framing. AI follows instructions; it rarely chooses the right question. Practice translating vague goals like “make a dashboard” into precise, checkable tasks such as “track weekly active users and cohort retention, then write a three-line narrative with drivers and caveats.” That skill of turning fog into a plan is a durable career advantage.
Creativity is another human edge. AI is excellent at variations and remixing patterns, but original direction—choosing the audience, message, and the unexpected connection across fields—still comes from people. Use AI to explore possibilities, then you decide what actually matters and why.
Finally, context, teamwork, judgment, and ethics remain stubbornly human. Reading the room, negotiating with classmates, persuading a client, balancing fairness and privacy, and taking responsibility for outcomes are hard to mechanize. AI can optimize, but humans choose values. You are accountable for the recommendation you make and the impact it has.
2) What the evidence says about capability expansion
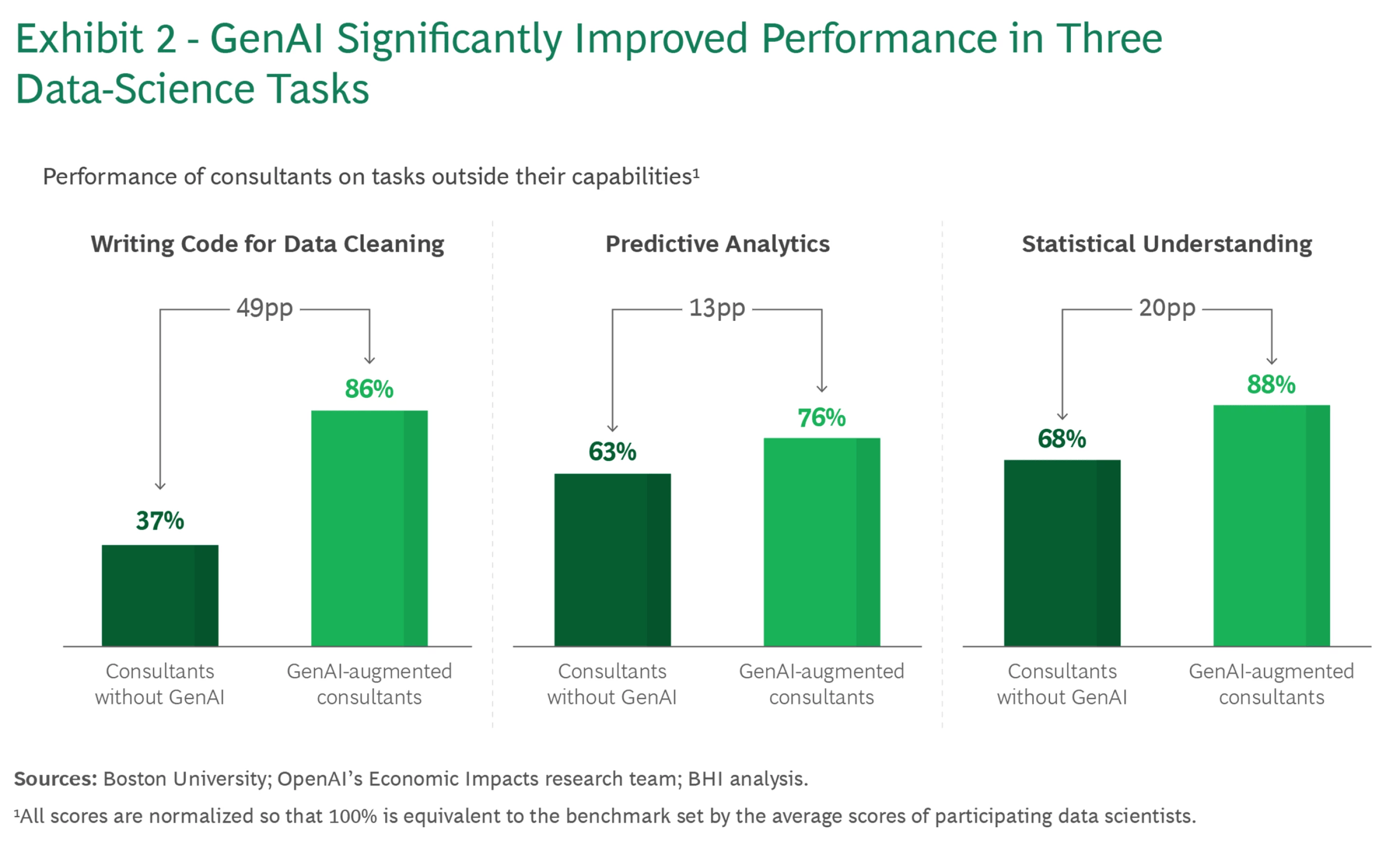
The figure compares people working without AI to those working with AI on tasks that were outside their comfort zones, with 100% set to the performance of professional data scientists. The headline result is that AI can immediately boost a beginner’s performance on structured tasks. In coding and data cleaning, for example, AI-augmented beginners reached roughly 86% of expert level, whereas those without AI hovered around the mid-30s. Translated into student life, this means you can merge messy datasets, fix obvious anomalies, and surface top customers or categories far faster—if you still sanity-check edge cases and data types.
The gains are more modest on fuzzier tasks like predictive analytics, especially when students paste the entire assignment into a single prompt. The groups who did best decomposed the work into steps (train/test split, features, baseline, metric), asked the model for intermediate artifacts, and verified them. A similar pattern shows up in statistical interpretation: when students requested pieces like residual plots or confusion matrices and inspected them, their results moved closer to expert practice. The practical reading is simple: AI can help you perform like a stronger student today, but performance is not the same as learning. Real understanding still requires practice, reflection, and feedback.
This matters for careers as well. If employers start recognizing AI fluency—through projects, portfolios, and practical certifications—you will need to show both that you can deliver results with AI and that you understand what the results mean. Being able to explain choices, defend assumptions, and spot failure modes will separate candidates who merely use AI from those who can be trusted with it.
3) How to prepare for a world where AI does many technical tasks better than people
Begin shifting from doing to directing. Expect AI to draft code, summarize readings, and generate baseline analyses. Your value moves upstream: define the goal, clarify constraints, set acceptance tests, and make the final call. Before you prompt, write a short spec that states the objective, the audience and data limits, and the conditions under which you will accept the result. Treat the model as a fast assistant inside a process you control.
Adopt the engineering mindset even if you never become a software engineer. Break big problems into small, testable steps; ask for intermediate artifacts you can check (schemas, sample rows, metrics); and only then assemble the final answer. Make verification routine rather than an afterthought: compare against a simple baseline, run a quick stress test or counterexample, ensure units and magnitudes make sense, and note sources and data lineage. Consistent, lightweight QA beats last-minute fixes.
Protect your intuition with manual mode. For your courses, make it a habit to work manually on purpose: push through problem sets on your own, draft essays from scratch, and code starting with a blank file. These efforts build the mental models you’ll need for exams, interviews, and real-world projects. Many instructors grade the reasoning process, and some assignments are explicitly no-AI. Honor those rules and use them to get stronger.
Finally, invest in learning agility and communication. Build a simple “learning stack” that might include one short tutorial, one article or paper, one conversation with a tutor or professor, and a one-page reflection. Track how quickly you can go from “don’t know” to “basic demo,” and aim to shorten that time over the semester. As AI multiplies outputs, synthesis and storytelling decide impact, so practice turning your work into a clear five-sentence brief: problem, method, result, limitation, and next step. This is the habit that will make you valuable in group projects now—and in internships soon.
References
- Sack et al., “GenAI Doesn’t Just Increase Productivity. It Expands Capabilities.” Boston Consulting Group, 2024.
- Simo, F., “Expanding economic opportunity with AI.” OpenAI, September 4, 2025.
