library(tidyverse)
library(stargazer)
library(broom)Homework 1
Linear Regression · Quarto Blogging
Directions
Submit your Quarto document for Part 1 to Brightspace using this filename format:
danl-320-hw1-LASTNAME-FIRSTNAME.qmd
(e.g.,danl-320-hw1-choe-byeonghak.qmd)
Due: February 11, 2026, 3:15 PM (ET)
Questions? Email Byeong-Hak bchoe@geneseo.edu.
Required R Packages
Part 1. Linear Regression
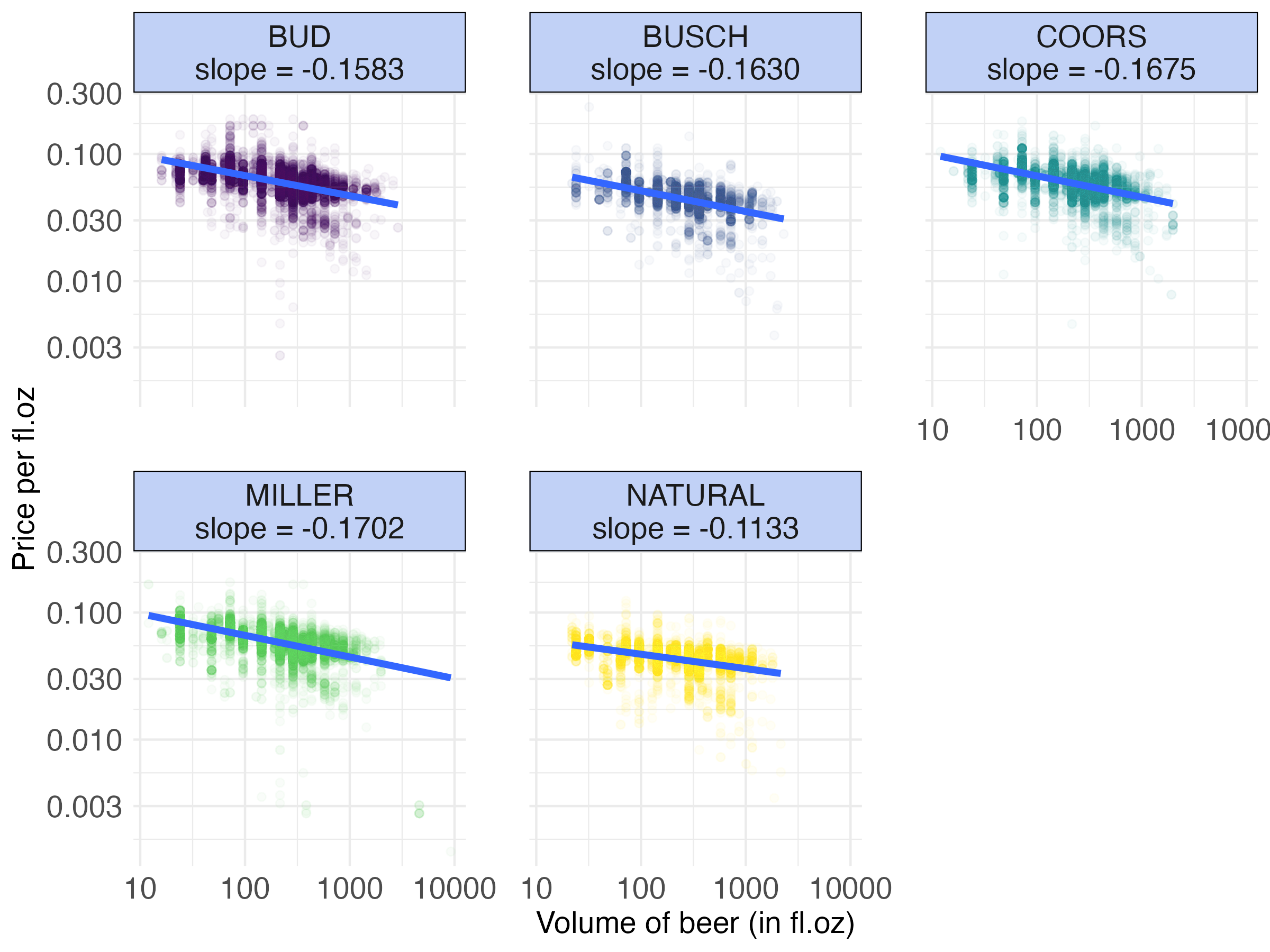
Consider the beer_markets data:
library(tidyverse)
beer_markets <- read_csv(
"https://bcdanl.github.io/data/beer_markets_all_cleaned.csv"
)