Lecture 11
Data Preparation and Management
September 23, 2024
Data Preparation and Management
A Simple Taxonomy of Data
Data Types Overview
- Categorical Data: Data that can be divided into distinct categories based on some qualitative attribute.
- Nominal Data
- Ordinal Data
- Numeric Data: Data that represents measurable quantities and can be subjected to mathematical algebra.
- Interval Data
- Ratio Data
A Simple Taxonomy of Data
Categorical Data - Nominal
| ID | Animal |
|---|---|
| 1 | Dog |
| 2 | Cat |
| 3 | Bird |
- Nominal Data: Categorical data where the categories have no intrinsic order or ranking.
- No Order: Categories are simply different; there is no logical sequence.
- Examples:
- Colors: Red, Blue, Green
- Types of Animals: Dog, Cat, Bird
A Simple Taxonomy of Data
Categorical Data - Ordinal
| ID | Education Level |
|---|---|
| 1 | Bachelor’s |
| 2 | Master’s |
| 3 | PhD |
Ordinal Data: Categorical data where the categories have a meaningful order or ranking.
Order Matters: Categories can be ranked or ordered, but the differences between categories are not necessarily uniform.
Examples:
- Education Levels: High School, Bachelor’s, Master’s, PhD
- Customer Satisfaction: Poor, Fair, Good, Excellent
A Simple Taxonomy of Data
Numeric Data - Interval
| ID | Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 70 |
| 2 | 80 |
| 3 | 90 |
Interval Data: Numeric data where the differences between values are meaningful, but there is no true zero point.
Meaningful Intervals: The difference between values is consistent.
No True Zero: Zero does not indicate the absence of the quantity.
Examples:
- Temperature (°F): Zero degrees does not mean no temperature.
- Time of Day in a 12-Hour Clock: Differences are meaningful, but there is no absolute zero.
A Simple Taxonomy of Data
Numeric Data - Ratio
| ID | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 160 | 55 |
| 2 | 175 | 70 |
| 3 | 170 | 65 |
Ratio Data: Numeric data with a true zero point, allowing for a full range of mathematical operations.
Meaningful Ratios: Comparisons like twice as much or half as much are valid.
True Zero: Zero indicates the absence of the quantity.
Examples:
- Height in Centimeters: Zero means no height.
- Weight in Kilograms: Zero means no weight.
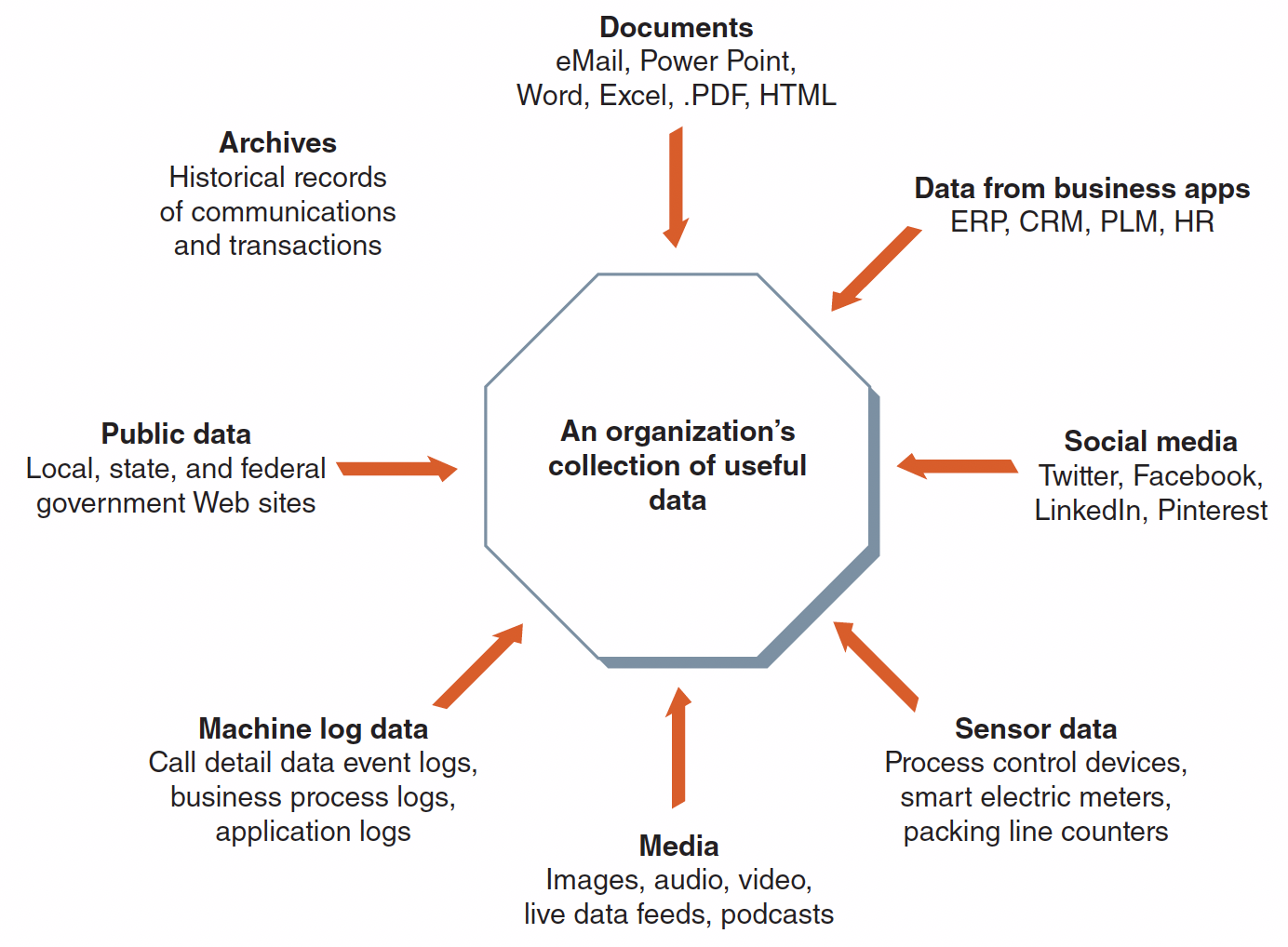
Sources of an Organization’s Data
Free Sources of Useful (Big) Data
Economics/Finance
| Data Source | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) | Provides access to data on inflation and prices, wages and benefits, employment, spending and time use, productivity, and workplace injuries | BLS |
| FRED (Federal Reserve Economic Data) | Provides access to a vast collection of U.S. economic data, including interest rates, GDP, inflation, employment, and more | FRED |
| Yahoo Finance | Provides comprehensive financial news, data, and analysis, including stock quotes, market data, and financial reports | Yahoo Finance |
| IMF (International Monetary Fund) | Provides access to a range of economic data and reports on countries’ economies | IMF Data |
| World Bank Open Data | Free and open access to global development data, including world development indicators | World Bank Open Data |
| OECD Data | Provides access to economic, environmental, and social data and indicators from OECD member countries | OECD Data |
Free Sources of Useful (Big) Data
Government/Public Data
| Data Source | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Data.gov | Portal providing access to over 186,000 government data sets, related to topics such as agriculture, education, health, and public safety | Data.gov |
| CIA World Factbook | Portal to information on the economy, government, history, infrastructure, military, and population of 267 countries | CIA World Factbook |
| U.S. Census Bureau | Portal to a huge variety of government statistics and data relating to the U.S. economy and its population | U.S. Census Bureau |
| European Union Open Data Portal | Provides access to public data from EU institutions | EU Open Data Portal |
| New York City Open Data | Provides access to datasets from New York City, covering a wide range of topics such as public safety, transportation, and health | NYC Open Data |
| Los Angeles Open Data | Portal for accessing public data from the City of Los Angeles, including transportation, public safety, and city services | LA Open Data |
| Chicago Data Portal | Offers access to datasets from the City of Chicago, including crime data, transportation, and health statistics | Chicago Data Portal |
Free Sources of Useful (Big) Data
Health, Climate/Environment, and Social Data
| Data Source | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Healthdata.gov | Portal to 125 years of U.S. health care data, including national health care expenditures, claim-level Medicare data, and other topics | Healthdata.gov |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | Portal to data and statistics on global health issues | WHO Data |
| National Centers for Environmental Information (NOAA) | Portal for accessing a variety of climate and weather data sets | NCEI |
| NOAA National Weather Service | Provides weather, water, and climate data, forecasts and warnings | NOAA NWS |
| FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) | Provides access to data on food and agriculture, including data on production, trade, food security, and sustainability | FAOSTAT |
| Pew Research Center Internet & Technology | Portal to research on U.S. politics, media and news, social trends, religion, Internet and technology, science, Hispanic, and global topics | Pew Research |
| Data for Good from Facebook | Provides access to anonymized data from Facebook to help non-profits and research communities with insights on crises, health, and well-being | Facebook Data for Good |
| Data for Good from Canada | Provides open access to datasets that address pressing social challenges across Canada | Data for Good Canada |
Free Sources of Useful (Big) Data
General Data Repositories
| Data Source | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) public data sets | Portal to a huge repository of public data, including climate data, the million song dataset, and data from the 1000 Genomes project | AWS Datasets |
| Gapminder | Portal to data from the World Health Organization and World Bank on economic, medical, and social issues | Gapminder |
| Google Dataset Search | Helps find datasets stored across the web | Google Dataset Search |
| Kaggle Datasets | A community-driven platform with datasets from various fields, useful for machine learning and data science projects | Kaggle Datasets |
| UCI Machine Learning Repository | A collection of databases, domain theories, and datasets used for machine learning research | UCI ML Repository |
| United Nations Data | Provides access to global statistical data compiled by the United Nations | UN Data |
| Humanitarian Data Exchange (HDX) | Provides humanitarian data from the United Nations, NGOs, and other organizations | HDX |
| Democratizing Data from data.org | A platform providing access to high-impact datasets, tools, and resources aimed at solving critical global challenges | Democratizing Data |
| Justia Federal District Court Opinions and Orders database | A free searchable database of full-text opinions and orders from civil cases heard in U.S. Federal District Courts | Justia |
Challenges of Big Data
Challenges of Big Data
Information Overload
- Difficulty in Finding Information
- Search Challenges: With so much data, traditional search methods become inefficient.
- Indexing Issues: Properly cataloging data to make retrieval efficient is complex.
- Trust Issues
- Data Validity: Users may question the accuracy and timeliness of available data.
- Source Credibility: Differentiating between reliable and unreliable data sources.
Challenges of Big Data
Information Overload
- Data from Diverse Sources
- Integration Complexity: Combining data from internal and external sources can be technically challenging.
- Data Formats: Managing different data types, such as structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data.
Challenges of Big Data
Compliance and Regulations
- Risk of Non-Compliance
- Legal Penalties: Organizations may face fines, sanctions, or legal action.
- Reputation Damage: Public trust can be eroded by non-compliance incidents.
- Impact on Organizations
- Operational Costs: Investing in compliance measures can be resource-intensive.
- Process Adjustments: Policies and procedures may need significant changes to meet regulatory standards.
Challenges of Big Data
Compliance and Regulations
- Need for Vigilance
- Evolving Laws: Regulations frequently update, requiring continuous monitoring.
- Employee Training: Staff must be educated on compliance requirements and best practices.
Challenges of Big Data
Privacy Concerns
- Data Harvesting
- Collection Methods: Corporations gather personal data through various means, often without explicit user consent.
- Scope of Data: Information ranges from basic demographics to detailed behavioral patterns.
- Extensive Profiling
- User Tracking: Monitoring online activities to build comprehensive profiles.
- Third-Party Sharing: Data sold or shared with other organizations, amplifying privacy risks.
Challenges of Big Data
Privacy Concerns
- Ethical Implications
- Consent and Transparency: Lack of clear communication about data usage.
- Right to Privacy: Debates over how much personal data companies should access and store.