Lecture 16
Web-scrapping with Python selenium
March 14, 2025
Web-scrapping with Python selenium
WebDriver
WebDriver is an wire protocol that defines a language-neutral interface for controlling the behavior of web browsers.
The purpose of WebDriver is to control the behavior of web browsers programmatically, allowing automated interactions such as:
- Extracting webpage content
- Opening a webpage
- Clicking buttons
- Filling out forms
- Running automated tests on web applications
Selenium WebDriver refers to both the language bindings and the implementations of browser-controlling code.
Driver
- Each browser requires a specific WebDriver implementation, called a driver.
- Web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge) do not natively understand Selenium WebDriver commands.
- To bridge this gap, each browser has its own WebDriver implementation, known as a driver.
- The driver handles communication between Selenium WebDriver and the browser.
- This driver acts as a middleman between Selenium WebDriver and the actual browser.
- Different browsers have specific drivers:
- ChromeDriver for Chrome
- GeckoDriver for Firefox
Interaction Diagram
- A simplified diagram of how WebDriver interacts with browser might look like this:
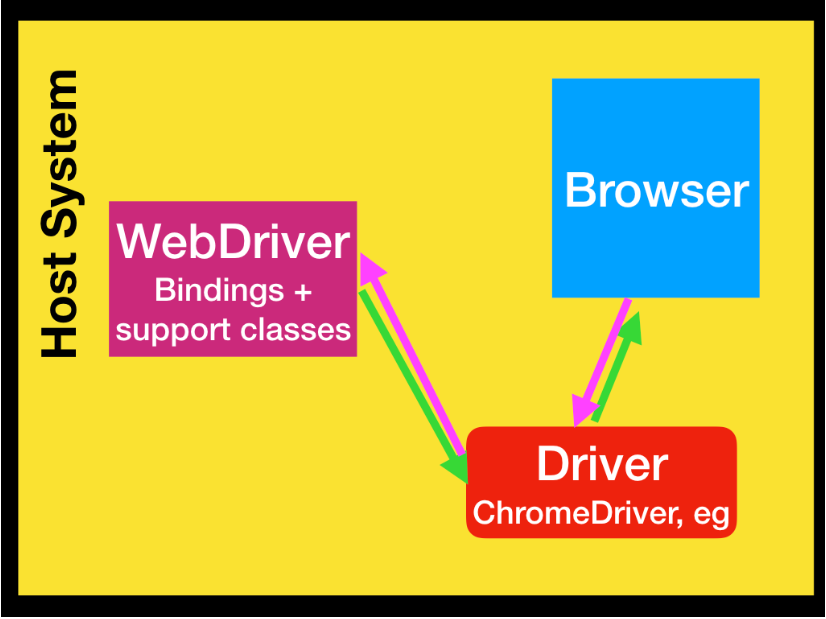
- WebDriver interacts with the browser via the driver in a two-way communication process:
- Sends commands (e.g., open a page, click a button) to the browser.
- Receives responses from the browser.
Setting up
- Install the Chrome or FireFox web-browser if you do not have either of them.
- I will use the Chrome.
- Install Selenium using
pip:- On the Spyder Console, run the following:
pip install selenium
- Selenium with Python is a well-documented reference.
Setting up - webdriver.Chrome()
- To begin with, we import (1)
webdriverfromseleniumand (2) theByandOptionsclasses.webdriver.Chrome()opens the Chrome browser that is being controlled by automated test software,selenium.
# Import the necessary modules from the Selenium package
from selenium import webdriver # Main module to control the browser
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By # Helps locate elements on the webpage
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options # Allows setting browser options
# Create an instance of Chrome options
options = Options()
options.add_argument("window-size=1400,1200") # Set the browser window size to 1400x1200
# Initialize the Chrome WebDriver with the specified options
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options) # Correct implementation
# Now you can use 'driver' to control the Chrome browserget() Method in WebDriver
get(url)fromwebdriveropens the specified URL in a web browser.- When using
webdriverin Google Chrome, you may see the message:- “Chrome is being controlled by automated test software.”
form_url = "https://qavbox.github.io/demo/webtable/"
driver.[?](form_url)
driver.close()
driver.quit()close()terminates the current browser window.quit()completely exits thewebdriversession, closing a browser window.
Inspecting Web Elements with find_element()
- Once the Google Chrome window loads with the provided URL, we need to find specific elements to interact with.
- The easiest way to identify elements is by using Developer Tools to inspect the webpage structure.
- To inspect an element:
- Right-click anywhere on the webpage.
- Select the Inspect option from the pop-up menu.
- In the
Elementspanel, hover over the DOM structure to locate the desired element.
Inspecting Web Elements with find_element()
- When inspecting an element, look for:
- HTML tag (e.g.,
<input>,<button>,<div>) used for the element. - Attributes (e.g.,
id,class,name) that define the element. - Attribute values that help uniquely identify the element.
- Page structure to understand how elements are nested within each other.
- HTML tag (e.g.,
Locating Web Elements by find_element() & find_elements()
Locating Web Elements by find_element()
- There are various strategies to locate elements in a page.
find_element(By.ID, "id")
find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "class name")
find_element(By.NAME, "name")
find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, "css selector")
find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "tag name")
find_element(By.LINK_TEXT, "link text")
find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT, "partial link text")
find_element(By.XPATH, "xpath")Selenium provides the
find_element()method to locate elements in a page.To find multiple elements (these methods will return a list):
find_elements()
find_element(By.ID, "")
find_element(By.ID, "")&find_elements(By.ID, ""):- Return element(s) that match a given ID attribute value.
- Example HTML code where an element has an ID attribute
form1:
find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "")
find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, "")&find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, ""):- Return element(s) matching a specific class attribute.
- Example HTML code with a
homebtnclass:
find_element(By.NAME, "")
find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, "")
find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, "")&find_elements(By.CSS_SELECTOR, ""):- Locate element(s) using a CSS selector.
- Inspect the webpage using browser Developer Tools.
- Locate the desired element in the Elements panel.
- Right-click and select Copy selector
- Let’s find out CSS selector for the Home button.
find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "")
find_element(By.LINK_TEXT, "")
find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT, "")
find_element(By.XPATH, "")
Understanding XPath
find_element(By.XPATH, "")&find_elements(By.XPATH, ""):- Return element(s) that match the specified XPath query.
- XPath is a query language for searching and locating nodes in an XML document.
- Supported by all major web browsers.
- Used in Selenium to find elements when ID, name, or class attributes are not available.
- Powerful for navigating complex HTML structures.
Basic XPath Syntax
//→ Selects elements anywhere in the document.tag_name→ HTML tag (input,div,span, etc.).@attribute→ Attribute name (id,class,aria-label, etc.).value→ Attribute’s assigned value.
Absolute vs. Relative XPath
- Absolute XPath → Defines the full path from the root node.
- Reliable if the webpage structure does not change.
- Relative XPath → Defines the path starting from a known element.
- More flexible—doesn’t break as easily if the structure changes.
Example: Finding a Table Element with XPath
- XPath can use attributes other than ID, name, or class to locate elements.
- Suppose we want to retrieve data from a second table on a webpage.
- The table contains multiple
<tr>(rows) and<th>(headers) without an easily identifiable ID or class. find_element(By.TAG_NAME, "")is not reliable due to multiple<tr>and<th>tags.
Extracting XPath from Developer Tools
- Inspect the webpage using browser Developer Tools.
- Locate the desired element in the Elements panel.
- Right-click and select Copy XPath.
- Example extracted XPath:
Finding an Element Using XPath
- Locate “Tiger Nixon” in the second table:
When to Use XPath
- Use XPath when:
- The element lacks a unique ID or class.
- Other locator methods (
By.ID,By.CLASS_NAME, etc.) don’t work.
- Limitations:
- XPath is less efficient than ID-based locators.
- Page structure changes may break XPath-based automation.
- For our tasks, however, XPath remains a reliable and effective method!
Retrieving Attribute Values with get_attribute()
get_attribute()extracts an element’s attribute value.- Useful for retrieving hidden properties not visible on the page.
Web-scrapping with Python selenium
Let’s do Classwork 9!
NoSuchElementException and WebDriverWait
NoSuchElementException and try-except blocks
from selenium.common.exceptions import NoSuchElementException
try:
elem = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "element_xpath")
elem.click()
except NoSuchElementException:
pass- When a web element is not found, it throws the
NoSuchElementException.try-exceptcan be used to avoid the termination of the selenium code.
- This solution is to address the inconsistency in the DOM among the seemingly same pages.
Explicit wait with time.sleep()
import time
# example webpage
url = "https://qavbox.github.io/demo/delay/"
driver.get(url)
driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="one"]/input').click()
time.sleep(5)
element = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="two"]')
element.textThe
time.sleep()method is an explicit wait to set the condition to be an exact time period to wait.In general, a more efficient solution than
time.sleep()would be to makeWebDriver()wait only as long as required.
Implicit wait with implicitly_wait()
driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="oneMore"]/input[1]').click()
driver.implicitly_wait(10) # Wait up to 10 seconds for elements to appear
element2 = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'delay')
element2.text- Implicit wait with
implicitly_wait()directs thewebdriverto wait for a certain measure of time before throwing an exception.- Applies globally for the lifetime of the driver session.
- Once this time is set,
webdriverwill wait for the element before the exception occurs.
Explicit wait with WebDriverWait and EC
- An explicit wait allows you to wait for a specific condition before continuing.
- Uses:
- Wait for elements to appear, be visible, or be clickable.
- More flexible and precise than implicit waits.
- To wait for
presence_of_element_located:
- To wait for
visibility_of_element_located:
Selenium with pd.read_html() for Table Scrapping
Selenium with pd.read_html() for Table Scrapping
Yahoo! Finance has probably renewed its database system, so that
yfinancedoes not work now.Yahoo! Finance uses web table to display historical data about a company’s stock.
Let’s use Selenium with
pd.read_html()to collect stock price data!
Selenium with pd.read_html() for Yahoo! Finance Data
import pandas as pd
import os, time, random
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from io import StringIO
# Set working directory
os.chdir('/Users/bchoe/.../lecture-code/')
# Launch Chrome browser
driver = webdriver.Chrome()StringIOturns that string into a file-like object, which is whatpd.read_json()expects moving forward.
# Load content page
url = 'https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/MSFT/history/?p=MSFT&period1=1672531200&period2=1743379200'
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(random.uniform(3, 5)) # wait for table to loadperiod1andperiod2values for Yahoo Finance URLs uses Unix timestamps (number of seconds since January 1, 1970),- 1672531200 → 2023-01-01
- 1743379200 → 2025-03-31
# Extract the <table> HTML element
table_html = driver.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, 'table').get_attribute("outerHTML")
# Parse the HTML table into a pandas DataFrame
df = pd.read_html(StringIO(table_html))[0].get_attribute("outerHTML"): gets the entire HTML from the WebElement.pd.read_html()parses HTML tables from a given URL or from raw HTML content, and returns a list of DataFrames.
Web-scrapping with Python selenium
Let’s do Classwork 10!