Lecture 3
Data Collection I: DataFrame; Spyder IDE; Scrapping Web-tables with pd.read_html()
February 9, 2026
🐼 Pandas Series and DataFrame
Pandas Series and DataFrame
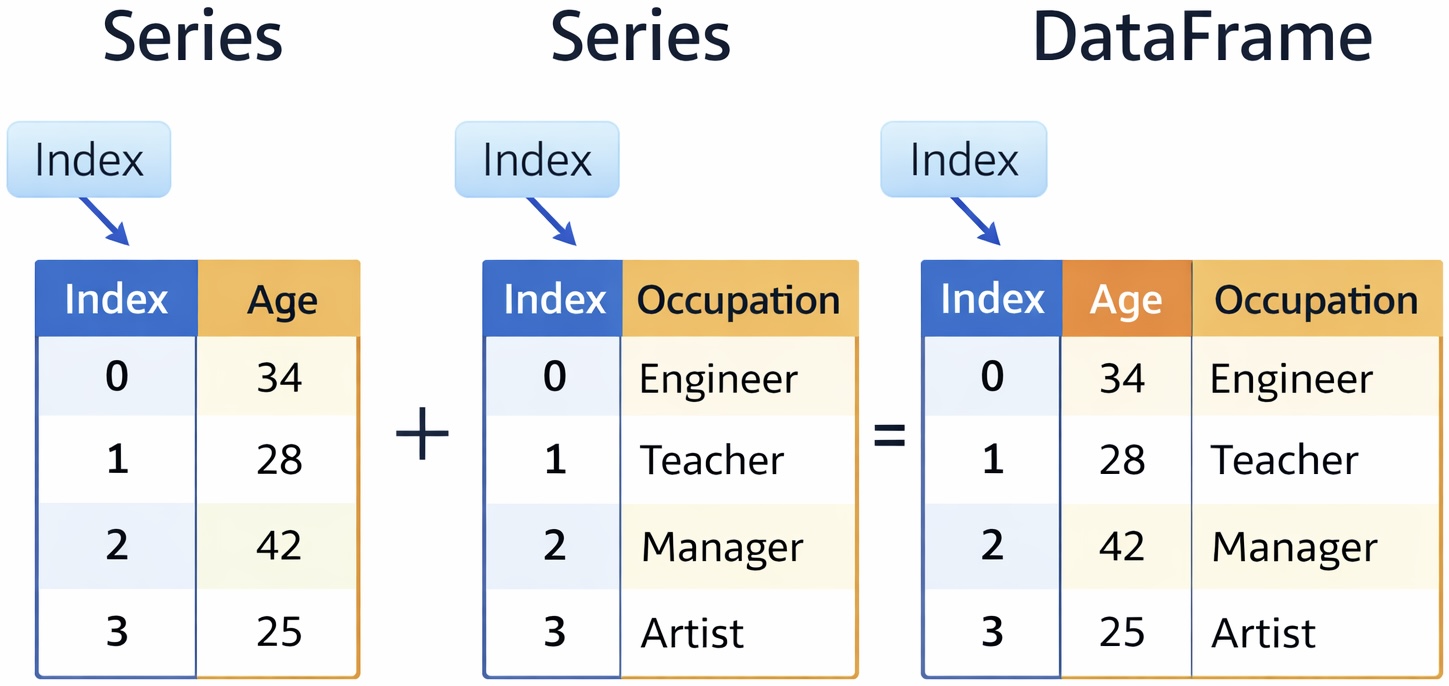
Series: A one-dimensional object containing a sequence of values (like a list).DataFrame: A two-dimensional table made of multipleSeriescolumns sharing a common index.
🧐 Observations in DataFrame
- Rows in a
DataFramerepresent individual units or entities for which data is collected.
- Examples:
- Student Information: Each row = one student
- Employee Information: Each row = one employee
- Daily S&P 500 Index Data: Each row = one trading day
- Household Survey Data: Each row = one household
- Student Information: Each row = one student
🏷️ Variables in DataFrame
- Columns in a
DataFramerepresent attributes or characteristics measured across multiple observations.
- Examples:
- Student Data:
Name,Age,Grade,Major
- Employee Data:
EmployeeID,Name,Age,Department
- Customer Data:
CustomerID,Name,Age,Income,HousingType
- Student Data:
Note
- In a
DataFrame, a variable is a column of data.
- In general programming, a variable is the name of an object.
✨ Tidy DataFrame
Variables, Observations, and Values

A
DataFrameis tidy if it follows three rules:- Each variable has its own column.
- Each observation has its own row.
- Each value has its own cell.
- Each variable has its own column.
A tidy
DataFramekeeps your data organized, making it easier to understand, analyze, and share in any data analysis.
🕸️ Spyder IDE
🟢 Anaconda Distribution
- Anaconda is a free Python distribution that includes Python, Conda (Python environment manager), and many commonly used data analytics packages.
- Install Anaconda from the official download page:
- Anaconda Distribution
- Click Get Started, then follow the installer steps for your operating system.
📄 What is a Python Script?
- A Python script (
*.py) is a plain-text file that contains Python code you can run from your computer (or an IDE like Spyder).- It is the standard format for writing reusable Python programs, such as data-cleaning pipelines, web scrapers, and automation tasks.
- Scripts are commonly used in real-world analytics and software projects.
- Compared to notebooks, scripts are typically better for organized, production-style code (functions, modules, and repeatable workflows).
- For data collection topics, we will write and run Python scripts mainly in Spyder, using Anaconda Distribution as our Python environment.
📝 Script Editor
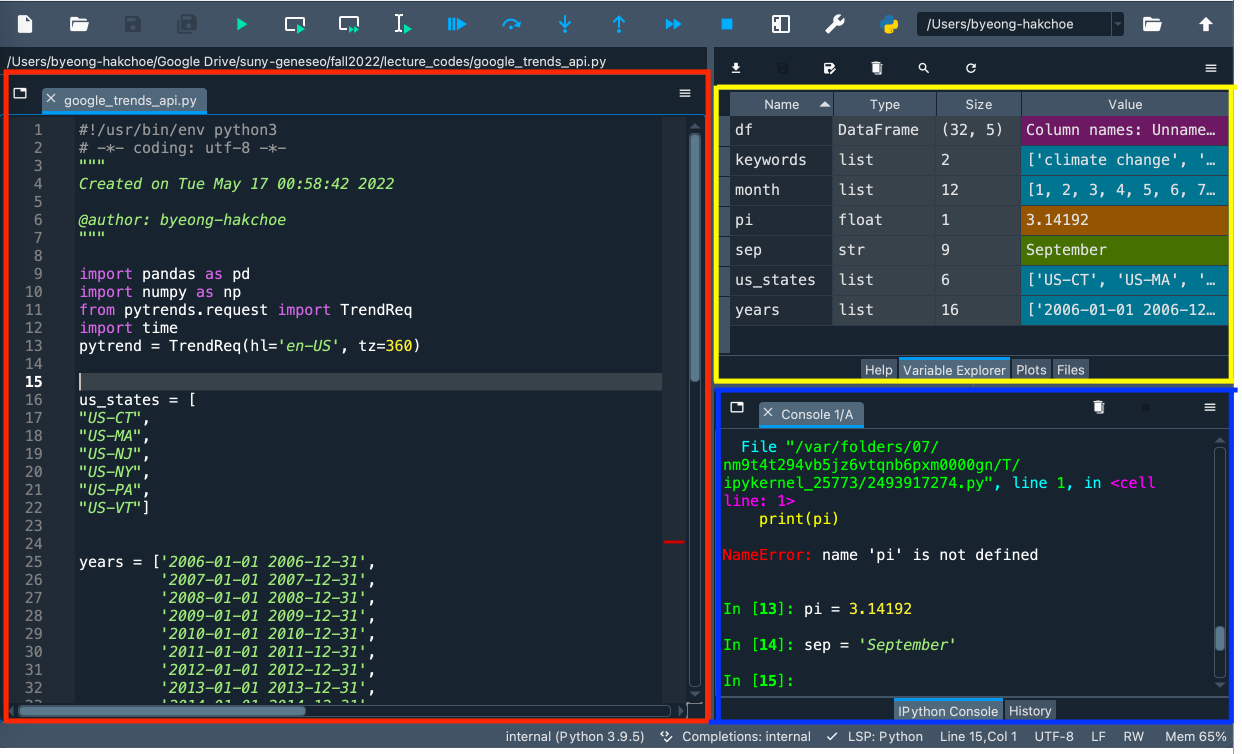
- From Script Editor (red box), we can create, open and edit files.
🖥️ Console Pane

- From Console Pane (blue box), we can interact directly with the Python interpreter, and type commands where Python will immediately execute them.
🔍 Variable Explorer

- From Variable Explorer (yellow box), we can see the values of variables, data frames, and other objects that are currently stored in memory.
📦️ Data Containers in Variable Explorer
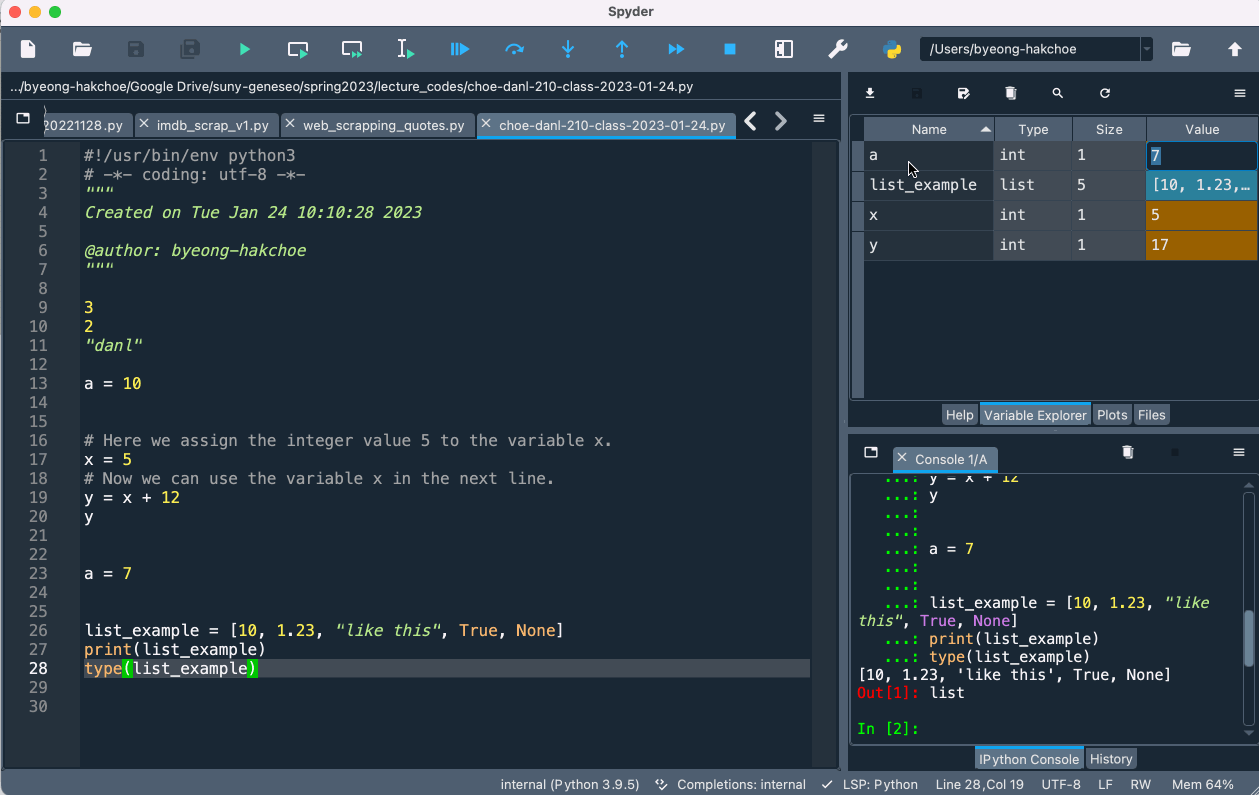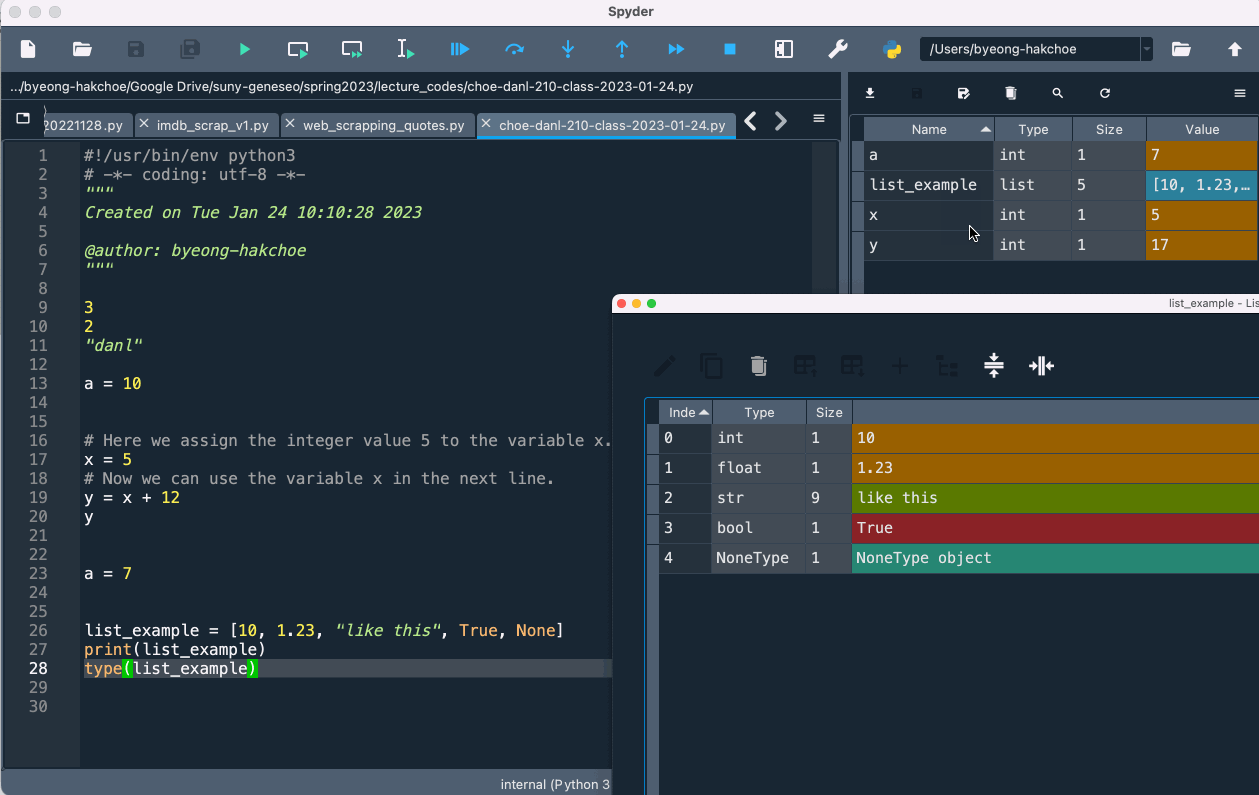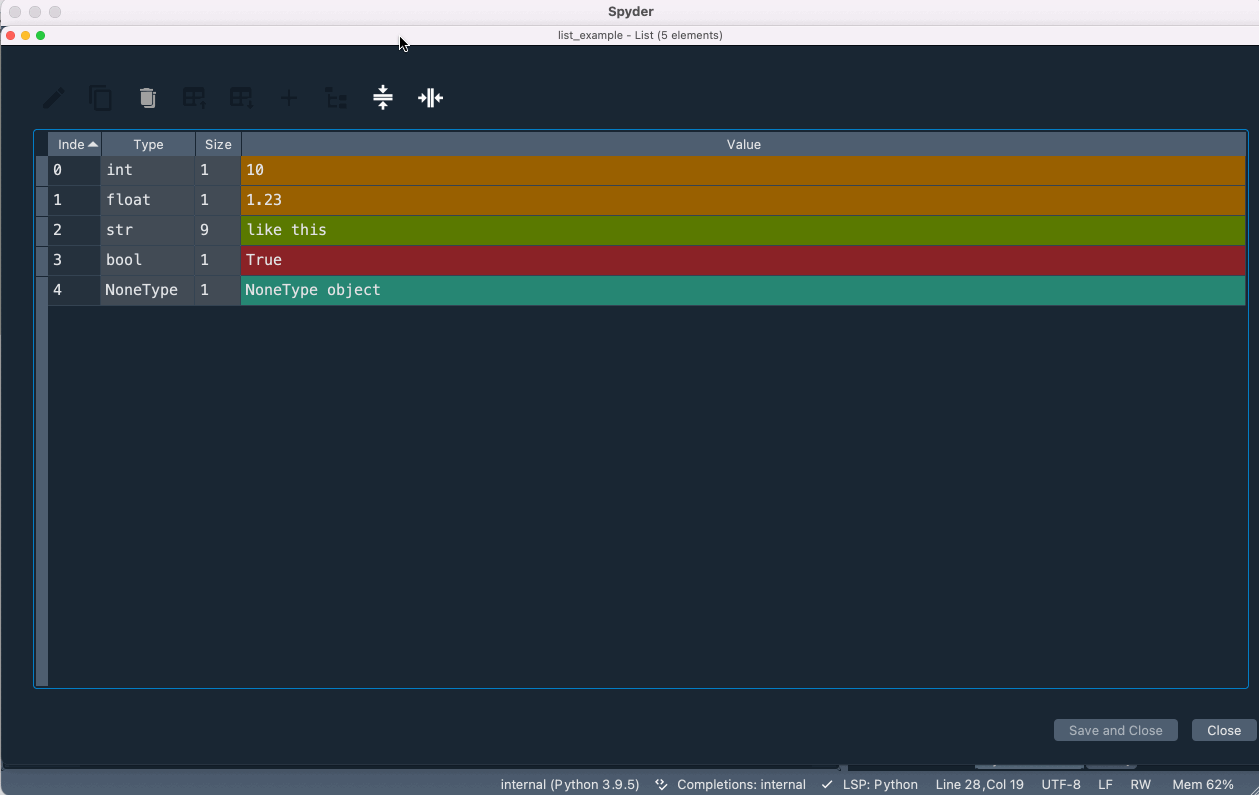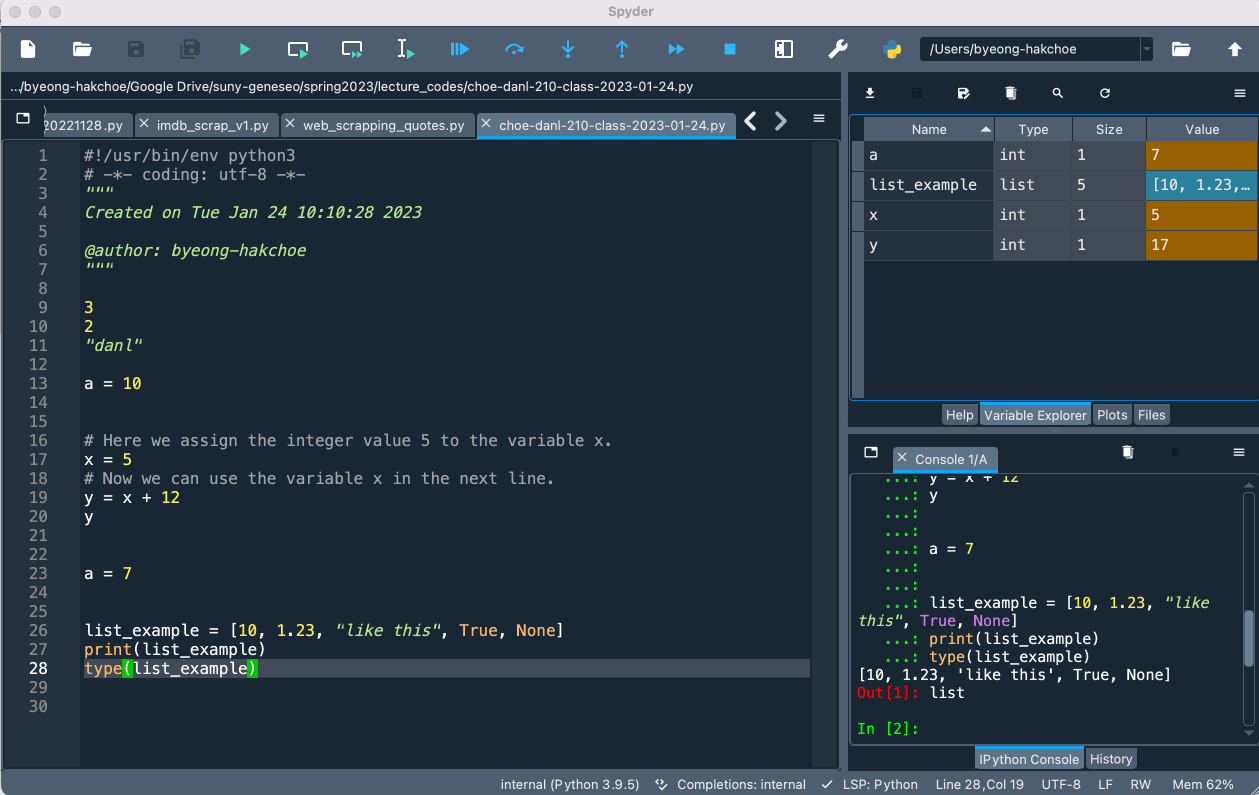
- If we doucle-click the objects such as
listandDataFrameobjects, we can see what data are contained in such objects.
⌨️ Keyboard Shortcuts
- General shortcuts
- Undo: Ctrl + z (command + z for Mac users)
- Redo: Ctrl + Shift + z (command + shift + z for Mac users)
- Selection: Ctrl + Shift + Arrow (⬆️ ➡️ ⬇️ ⬅️)
- Page Up/Down: Fn + ⬆️ / ⬇️
- Default shortcuts
- Comment (
#): Ctrl + 1 (command + 1 for Mac users) - Block-comment: Ctrl + 4 (command + 4 for Mac users)
- Run selection (or a current line): F9
- Run cell: Ctrl + Enter (
# %%defines a cell)
- Comment (
🌐 Scrapping web tables with pd.read_html()
🌍 Scrapping Tables with pd.read_html()
- Let’s scrap the two tables in the following webpage:
import pandas as pd
url = "https://www.nps.gov/orgs/1207/national-park-visitation-sets-new-record-as-economic-engines.htm"
tables = pd.read_html(url)
len(tables)
df_0 = tables[0]read_html()read HTML tables into a list ofDataFrameobjects.
🏷️ Setting Column Names
- How can we set the first row of a DataFrame as its column names?
- How can we remove the first row ?
df_0 = tables[0]
df_0.columns = df_0.iloc[0] # Set the first row as column names
df_0 = df_0.iloc[1:] # Keeps rows from position 1 onward✅ What is DataFrame.iloc[]?
DataFrame.iloc[...]is integer-location indexing:- It selects rows by position (0, 1, 2, …), not by index labels.
- Slicing works with
DataFrame.iloc[]
df_0.iloc[0]returns the first row (position 0) as a Series.
⚙️ Dot Operators, Methods, and Attributes
⚫ Dot operator
- The dot operator (
DataFrame.) is used for an attribute or a method on objects.
🛠️ Method
- A method (
DataFrame.METHOD()) is a function that we can call on aDataFrameto perform operations, modify data, or derive insights.- e.g.,
df.info()
- e.g.,
🏷️ Attribute
- An attribute (
DataFrame.ATTRIBUTE) is a property that provides information about theDataFrame’s structure or content without modifying it.- e.g.,
df.columns
- e.g.,
📑 Getting a Summary of a DataFrame
- Every
DataFrameobject has a.info()method that provides a summary of a DataFrame:- Variable names (
.columns) - Number of observations and variables (
.shape) - Number of non-missing values in each variable (
.count())- Pandas often displays missing values as
NaN.
- Pandas often displays missing values as
- Variable names (
📍 Absolute Pathnames
An absolute pathname tells the computer the exact location of a file, starting from the very top folder of your computer.
- This location never changes, no matter where you are working in Python.
- This location never changes, no matter where you are working in Python.
In Python, you can see the working directory — the folder where Python is currently “looking” for files — by running
os.getcwd()in the Console.Examples of an absolute pathname for
custdata_rev.csv:- On a Mac:
/Users/user/documents/data/custdata_rev.csv
- On Windows:
C:\\Users\\user\\Documents\\data\\custdata_rev.csv- Note: In Windows, we use double backslashes (
\\) because a single backslash (\) is treated as a special character in Python.
- Note: In Windows, we use double backslashes (
- On a Mac:
🔗 Relative Pathnames
- A relative pathname specifies the location of a file relative to the working directory.
- Examples of a relative pathname for
custdata_rev.csv:- Absolute pathname:
/Users/user/documents/data/custdata_rev.csv - Working directory:
/Users/user/documents/
- Relative pathname:
data/custdata_rev.csv
- Absolute pathname:
📍📁 Finding the Absolute Path of a File/Folder
Windows 11
- Step 1: Navigate to your folder using File Explorer.
- Step 2: Right-click the desired file or folder.
- Step 3: Click Copy as path.
- Step 4: Paste the path into your Python script (Ctrl + V).
- Step 5: Adjust backslashes in the path:
- Option 1: Replace backslashes (
\) with forward slashes (/). - Option 2: Replace single backslashes (
\) with double backslashes (\\).
- Option 1: Replace backslashes (
Mac
- Step 1: Navigate to your folder using Finder.
- Step 2: Select the file or folder by clicking on it.
- Step 3: Copy the path (Option + Command + C).
- Step 4: Paste the path into your Python script (Command + V).
📑 CSV Files
- A CSV (comma-separated values) file is a plain text file where each value is separated by a comma.
- CSV files are widely used for storing data from spreadsheets and databases.
💾 Exporting a DataFrame as a CSV File with to_csv()
- To export
DataFrameas a CSV file, we use theto_csv()method.- Before exporting, you can set the working directory (WD) to organize and manage the location of CSV files.
- Create a
datadirectory within your WD. This helps in keeping your data analysis and exports well-organized.
# Import the os module to interact with the operating system
import os
# Set the working directory path
wd_path = 'ABSOLUTE_PATHNAME_OF_YOUR_WORKING_DIRECTORY' # e.g., '/Users/bchoe/Documents/DANL-210'
os.chdir(wd_path) # Change the current working directory to wd_path
os.getcwd() # Retrieve and return the current working directory
# index=False to not write the row index in the CSV output
df_0.to_csv('data/table.csv', index =False)Scrapping Tables with pd.read_html()
Let’s do Classwork 3!
💬 Comments, Code Cells, and Keyboard Shortcuts
The
#mark is Spyder’s comment character.It is recommended to use a coding block (defined by
# %%) with block commenting (Ctrl/command + 4) for separating code sections.To set your keyboard shortcuts,