Lecture 2
Python Fundamentals
January 23, 2026
Python Basics
Values, Variables, and Data Types
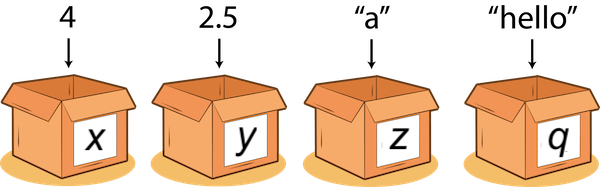
A value is a literal such as a number or text.
Examples of values:
352.3→ float22→ int"Hello World!"→ str
Variables
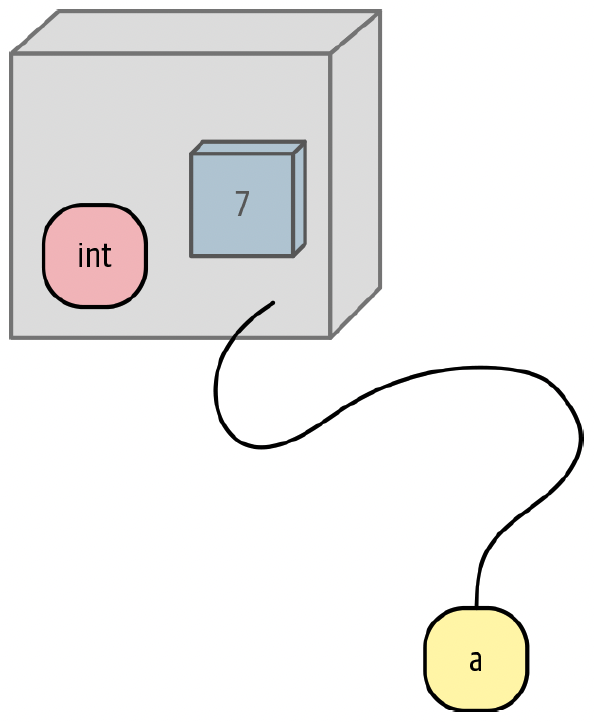
- A variable is a name that refers to a value.
- Think of a variable like a label attached to a value.
- A variable is just a name (not the value itself).
Objects
- Sometimes you will hear variables referred to as objects.
- Everything that is not a literal (like
10) is an object in Python.
Assignment ( = )
# Here we assign the integer value 5 to the variable x.
x = 5
# Now we can use the variable x in the next line.
y = x + 12
y- In Python,
=means assignment:- Right side is evaluated first
- The result is assigned to the left side
Note
✅ In math, = often means “equal.”
✅ In Python, = means “store this value in the variable.”
✍️💬 Code and comment style
- Two guiding principles:
- Make things easy for your future self
- Assume you will forget details later → write it down now
- In Python, the comment character is
#- Anything after
#is ignored by the interpreter - Put comments right above the code they describe
- Anything after
- Use Markdown/text cells to explain:
- What the code cell is doing,
- Any assumptions/choices,
- How to interpret output.
⌨️ Most Useful Google Colab Shortcuts
Windows
- Ctrl + Enter: Run cell
- Alt + Enter: Run cell and add new cell below
- Ctrl + /: Comment current line
- Ctrl + Z: Undo
- Ctrl + Shift + Z: Redo
- Shift + ⬅️⬆️⬇️➡️: Select text
- Shift + Ctrl + ⬅️⬆️⬇️➡️: Select to the beginning/end of the line
Mac
- command + return: Run cell
- option + return: Run cell and add new cell below
- command + /: Comment current line
- command + Z: Undo
- command + shift + Z: Redo
- shift + ⬅️⬆️⬇️➡️: Select text
- shift + command + ⬅️⬆️⬇️➡️: Select to the beginning/end of the line
Types
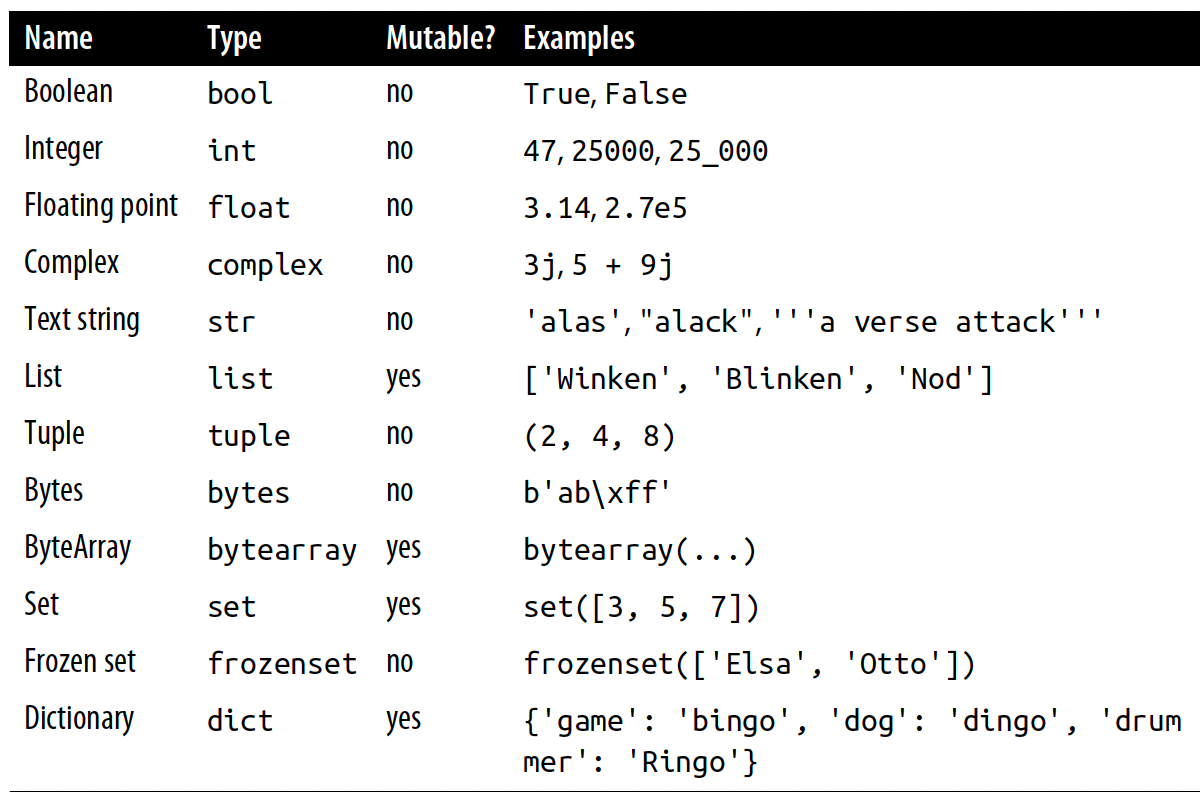
The Type column shows Python’s official type name.
Mutable?
- ✅ mutable → can be changed after creation
- ❌ immutable → cannot be changed after creation
One List, Many Types
- Common built-in types:
int(e.g.,10)float(e.g.,1.23)str(e.g.,"hello")bool(e.g.,True)NoneType(e.g.,None)
- A list can contain mixed types.
Square Brackets [] in Python
- Use
[]to create a list - Use
[]to access an element by index
Curly Braces {} in Python
{}is used to denote a set or a dictionary- Use
{}for sets and dictionaries
Parentheses () in Python
- Use
()for tuples - Use
()to pass arguments into functions
🧺 Data Containers in Python—List and Tuple
✅ List
- Stores multiple values in an ordered sequence
- 🔄 Mutable: You can change it after creation
✅ Tuple
- Stores multiple values in an ordered sequence
- 🔒 Immutable: Cannot be changed after creation
🗂️ Data Containers in Python—Dictionaries
city_to_temp = {
"Paris": 28,
"London": 22,
"New York": 18,
"Seoul": 29,
"Rochester": 10
}
city_to_temp["Paris"] # 🔍 look up a value by key
city_to_temp["London"] = 32 # ✏️ update a value
city_to_temp.keys() # 🔑 all keys
city_to_temp.values() # 🌡️ all values
city_to_temp.items() # 🧾 (key, value) pairs- Stores values as key→value pairs
- Keys are used for fast lookup
- Useful when you want to create associations (“mapping”)
Running on Empty
Being able to create empty containers is sometimes useful, especially when using loops (e.g.,
for,while).Q. What is the type of an empty list?
Operators ➕➖✖️➗
Operators Also Work for Lists and Strings
Casting Variables
- Casting changes type using built-in functions:
int(),float(),str()- If we try these, Python will do its best to interpret the input and convert it to the output type we’d like and, if they can’t, the code will throw a great big error.
- Q. Classwork 2.1
✅❓ Booleans, Conditions, and if Statements
Booleans
Boolean Operators
Here, both x and y are boolean.
- Existing booleans can be combined by a boolean operator, which create a boolean when executed.
⚖️ Comparison Operators
Here, both x and y are variables.
🟰 The Equality Operator ==
The
==is an operator that compares the objects on either side and returnsTrueif they have the same valuesQ. What does
not (not True)evaluate to?
Conditions → Boolean Expressions
- A condition is an expression that returns
TrueorFalse.
🚦🧾 Condition and if Statements
name = "Geneseo"
score = 99
if name == "Geneseo" and score > 90:
print("Geneseo, you achieved a high score.")
if name == "Geneseo" or score > 90:
print("You could be called Geneseo or have a high score")
if name != "Geneseo" and score > 90:
print("You are not called Geneseo and you have a high score")- The real power of conditions comes when we start to use them in more complex examples, such as
ifstatements.
The in Keyword: Membership Test
inchecks whether something exists inside a list, string, etc.Q. Check if “a” is in the string “Wilson Ice Arena” using
in. Is “a” in “Anyone”?
if-else Chain
if Statements with in
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
favorite = "banana"
if favorite in fruits:
print(f"{favorite} is available!")
else:
print(f"{favorite} is not in the list.")- The keyword
inlets you check whether a value is present in a list, string, or other iterable.
- This works seamlessly inside an
if-elsestructure.
- Useful for membership tests such as:
- Validating if a company is in a stock list
- Seeing if a word exists in a sentence
- Validating if a company is in a stock list
f-Strings (Formatted Strings) in Python
An f-string is a convenient way to create strings that include variable values directly inside the text.
✅ Key idea: Put an f before the quotation marks, then use {} to insert variables.
Indentation
In Python, indentation is required for code blocks, such as code inside:
- a user-defined function (
def ...), - a conditional (
if / elif / else), - a loop (
for / while).
- a user-defined function (
Indentation is how Python knows which lines belong to a block.
It tells the interpreter what should run inside the block (e.g., inside anif) and what should run after the block ends.Standard Python style is 4 spaces per indentation level.
- In Google Colab, you might see 2 spaces.
✂️ Slicing Methods with Strings and Lists
✂️ Slicing Methods
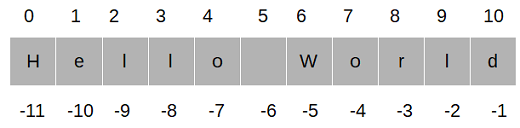
Slicing methods can apply for strings, lists, and DataFrames.
With slicing methods, we can get a subset of the data object.
Python is:
- zero-indexed (things start counting from 0)
- left inclusive
- right exclusive when we specify a range
🧩 Slicing Patterns
- Slice format:
[start : end : step]startis includedendis excludedstepcontrols how many characters to skip
- ✅ Important (when you “skip” numbers)
If you omitstartorend, Python fills them in automatically:- If
startis missing → slicing starts from the beginning - If
endis missing → slicing goes to the end - Example:
letters[::2]means “from the beginning to the end, taking every 2nd character.”
- If
📏 Length of a String and a List
- Both strings and list objects support
len() len()tells you how many items/characters are stored
✂️🧾 Slicing with Lists
- Python is
- a zero-indexed language (things start counting from zero);
- left inclusive;
- right exclusive when we are specifying a range of values.
✂️🧾 Slicing with Lists
- We can think of items in a list-like object as being fenced in.
- The index represents the fence post.
🔢 Get an Item by [index]
✂️ Get an Item with a Slice
⚙️ Functions, Arguments, and Parameters
⚙️ Functions
Common built-in functions you will use often:
type()→ data typelen()→ length
max()→ largest valuesum()→ total
- A function can take inputs (called arguments) and return an output.
- Python also lets you define your own functions with the
defkeyword. - Later, we will use such user-defined function together with pandas.
⚙️📥 Functions, Arguments, and Parameters
print("Cherry", "Strawberry", "Key Lime")
print("Cherry", "Strawberry", "Key Lime", sep = "!")
print("Cherry", "Strawberry", "Key Lime", sep=" ")To call a function, write its name followed by parentheses:
function_name(...)
Inside the parentheses, you provide arguments (inputs), separated by commas.
A parameter is the name used in the function definition for an expected input
- Example:
sepis a parameter ofprint().
- Example:
A default argument is the value used automatically if you do not specify it.
- For
print(), the default separator is a space:sep = " ".
- For
🔁 Loop with while and for
➕= Updating a Variable with +=
+=is a shortcut assignment operator- It means: take the current value and add something to it
- E.g.,:
count += 1means the same thing ascount = count + 1.
🔄⏳ Repeat with while
How this loop works
- Start with
count = 1. - Check the condition:
count <= 5- If it is
True, run the loop body.
- If it is
- Print the current value of count.
- Update count using
count += 1. - Go back to step 2 and repeat.
- The loop stops when
count <= 5becomesFalse.
🙋⌨️ Asking the user for input
stuff = input()
# Type something and press Return/Enter on Python Console
# before running print(stuff)
print(stuff)input()pauses the program and waits for the user to type something.- Whatever the user types is returned as a string.
- This is useful when you want to make your code interactive.
🛑🔁 Cancel an Infinite Loop with break
while True:
user_input = input("Enter 'yes' to continue or 'no' to stop: ")
if user_input.lower() == 'no':
print("Exiting the loop. Goodbye!")
break
elif user_input.lower() == 'yes':
print("You chose to continue.")
else:
print("Invalid input, please enter 'yes' or 'no'.")Whileloop is used to execute a block of code repeatedly until given boolean condition evaluated toFalse.while Truecreates an infinite loop
- The loop runs forever unless you stop it using
break breakexits the loop immediately
⏭️🔁 Skip Ahead with continue
while True:
value = input("Integer, please [q to quit]: ")
if value == 'q': # quit
break
number = int(value)
if number % 2 == 0: # an even number
continue
print(number, "squared is", number*number)continueskips the rest of the loop body for the current iteration- Then Python jumps back to the top of the loop
🔁🔎 Iterate with for and in
- Use a
forloop when you want to go through each item in:- a string
- a list
- a range (
range()) - or any iterable object
🔁🚶 Repeat with a for Loop
for loop syntax (the pattern)
How this loop works
- Take the first item in
lst_nums→ setnum = 0→ runprint(num) - Take the next item → set
num = 1→ runprint(num) - Repeat for
2,3,4 - Stop after the last item
Two Ways to Loop Through an Iterable
- Which one do you prefer?
🔢 Generate Number Sequences with range()
range()creates a sequence of integers without storing a full list- This is memory-efficient and very common in
forloops
- Syntax is similar to slicing:
range( start, stop, step )startdefaults to 0stepdefaults to 1- the sequence stops right before stop
🔢🧾 Get Index + Value with enumerate()
enumerate()gives you two things while looping:- the index (
i) - the value (
fruit)
- the index (
- Very handy when you want to label, number, or track positions.
- Syntax:
enumerate(iterable, start=0)iterablecan be a list, tuple, string, etc.startcontrols the first index (default is 0)
🛑🔂 Cancel a for Loop with break
breakexits the loop immediately
⏭️🔂 Skip in a for Loop with continue
continueskips the current iteration and moves to the next one
🔄 Loop Control: continue, pass, break
for num in range(1, 6):
if num == 2:
continue # skip printing 2
if num == 3:
pass # do nothing, move on
if num == 4:
break # exit the loop
print(num)continue→ skips to the next iteration
pass→ does nothing (useful as a placeholder)
break→ exits the loop completely
📋📘⚡ List and Dictionary Comprehensions
❓📋 What is List Comprehension?
❓📘 What is Dictionary Comprehension?
- A concise way to create or modify dictionaries.
- Syntax:
{key_expression:value_expressionforiteminiterableifcondition}
- Creating a Dictionary of Squares:
- Filtering Dictionary Items:
my_dict = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4}
filtered_dict = {k: v for k, v in my_dict.items() if v != 2}- Swapping Keys and Values:
🛠️ Modifying Lists and Dictionaries
The . (dot) Operator on an Object
text = "GeNeSeO"
print(text.lower()) # method on a string object
print(text.upper()) # another string method- In Python, the dot operator (
.) means:
“go inside this thing and access one of its members.” - Many data types come with built-in methods you can call using the dot operator.
- Example: For strings,
.lower()is a method that returns a lowercase version of the string. - ✅ Here,
textis a string object, andtext.lower()means:
“use the lower() method that belongs to the string type.”
🔧 Adding an Item to a List
🔧 Deleting Items in a List
remove(): Deletes the first occurrence of value in the list.
- List Comprehension: Removes items based on a condition.
delstatement: Deletes an item by index or a slice of items.
🔧 Adding/Updating Items in a Dictionary
🔧 Deleting Items in a Dictionary
- Dictionary Comprehension: Removes items based on a condition.
delstatement: Deletes an item by key.
⚠️🛡️ Handle Errors with try and except
⚠️️ Errors
short_list = [1, 2, 3]
positions = [0, 1, 5, 2] # 5 is out of range
for i in positions:
print(short_list[i])- If we don’t write our own exception handler, Python will:
- print an error message (a traceback) explaining what went wrong, and
- stop the program.
🛡 Exception Handlers (Why we need them)
- In Python, when something goes wrong, an exception is raised.
- If we’re running code that might fail, we can add an exception handler so the program can respond nicely instead of crashing.
- Common examples:
- Using an index that’s out of range for a list/tuple
- Looking up a key that doesn’t exist in a dictionary
⚠️🛡️ Handle Errors with try and except
short_list = [1, 2, 3]
positions = [0, 1, 5, 2] # 5 is out of range
for i in positions:
try:
print(short_list[i])
except:
print("Index error:", i, "is not between 0 and", len(short_list) - 1)- Use
tryto run code that might fail, andexceptto handle the error gracefully.- If an error occurs, Python raises an exception and runs the
exceptblock. - If no error occurs, Python skips the
exceptblock.
- If an error occurs, Python raises an exception and runs the
- Q. Classwork 2.9
📦⬇️ Importing and Installing Modules, Packages, and Libraries
📦⬇️ Importing Modules, Packages, and Libraries
Python is a general-purpose programming language and is not specialized for numerical or statistical computation.
The core libraries that enable Python to store and analyze data efficiently are:
pandasnumpy
🐼 pandas

pandasprovidesSeriesandDataFrameswhich are used to store data in an easy-to-use format.
🔢 numpy

numpy, numerical Python, provides the array block (np.array()) for doing fast and efficient computations;
📥🧾 import statement
A module is basically a bunch of related codes saved in a file with the extension
.py.A package is basically a directory of a collection of modules.
A library is a collection of packages
We refer to code of other module/package/library by using the Python
importstatement.
- This makes the code and variables in the imported module available to our programming codes.
📥🏷️ import statement with as or from
Keyword as
- We can use the
askeyword when importing the module/package/library using its canonical names.
🛠️📦 pip tool
🧩 The . (dot) Operator on a Library
- In Python, the dot operator (
.) means:
“go inside this thing and access one of its members.”module.name→ access something defined inside the module
object.attributeorobject.method()→ access a property or function of an object
Example 1: import sys
import sys
print(sys.version) # attribute: Python version info
print(sys.path) # attribute: module search paths✅ Here, sys is a module, and sys.version and sys.path are things inside the sys module.
Example 2: import datetime
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now() # module.class.method()
today = datetime.date.today() # module.class.method()datetime(left side) is the moduledatetime.datetimeis a class inside the module
.now()is a method you can call from that class
- A class is a blueprint for creating objects that bundles attributes and methods together.
Common Patterns to Remember
module.somethingmodule.class_name.method_name()object.method_name()
Read it like:
“start with the thing on the left → use
.to reach something inside → then (maybe) call it with()”