Lecture 2
Prologue; DANL Tools; Building a Website; Markdown
January 24, 2025
Prologue
Why Data Analytics?
- Fill in the gaps left by traditional business and economics classes.
- Practical skills that will benefit your future career.
- Neglected skills like how to actually find datasets in the wild and clean them.
- Data analytics skills are largely distinct from (and complementary to) the core quantitative works familiar to business undergrads.
- Data visualization, cleaning and wrangling; databases; machine learning; etc.
- In short, we will cover things that I wish someone had taught me when I was undergraduate.
You, at the end of this course

Why Data Analytics?
- Data analysts use analytical tools and techniques to extract meaningful insights from data.
- Skills in data analytics are also useful for business analysts or market analysts.
- Breau of Labor Statistics forecasts that the projected growth rate of the employment in the industry related to data analytics from 2021 to 2031 is 36%.
- The average growth rate for all occupations is 5%.
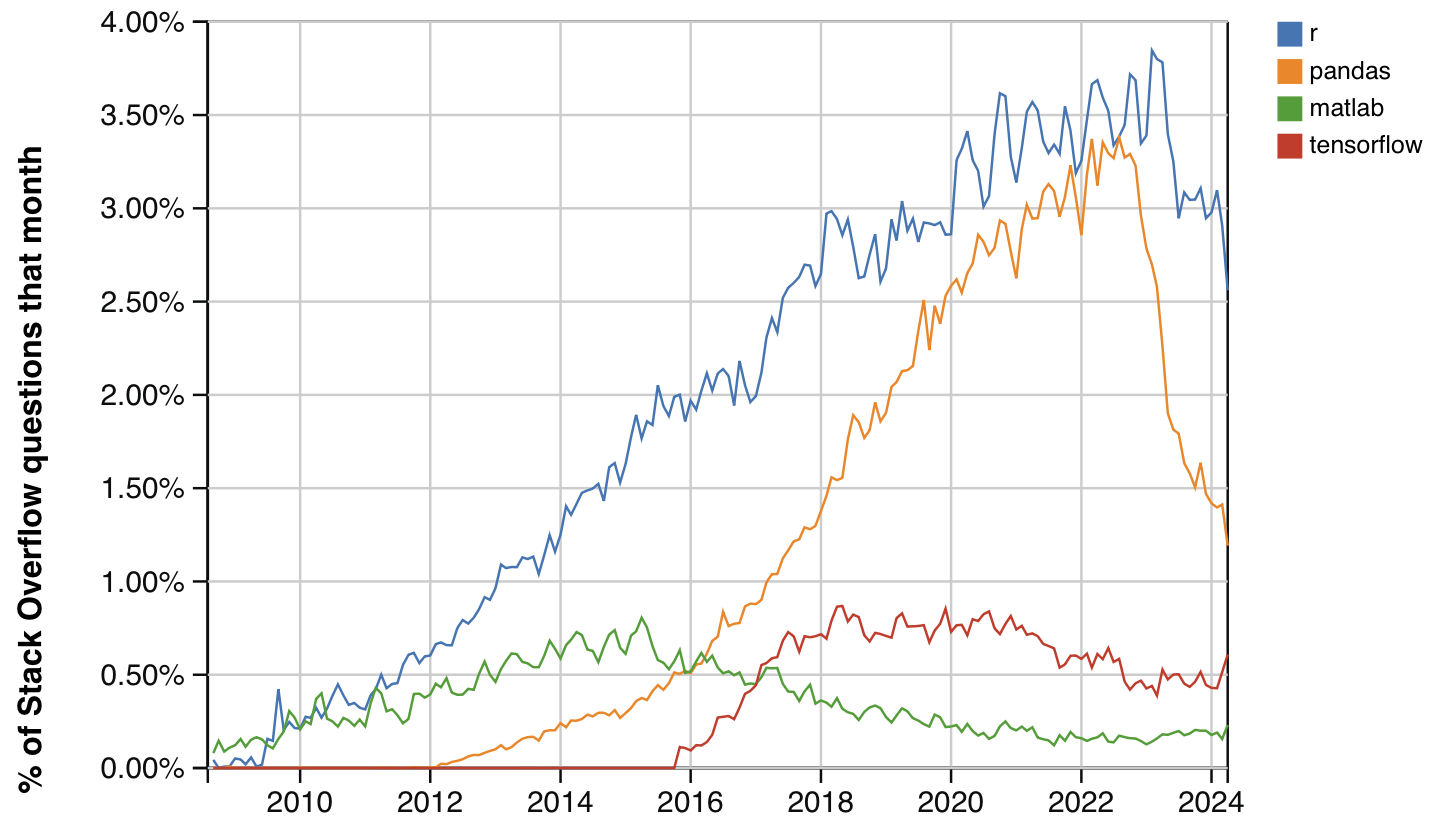
The State of the Art
Generative AI and ChatGPT
Data Science and Big Data Trend
From 2008 to now
Programmers in 2025

The State of the Art
Generative AI and ChatGPT
- Users around the world have explored how to best utilize GPT for writing essays and programming codes.
- Is AI a threat to data analytics?
- Fundamental understanding of the subject matter is still crucial for effectively utilizing AI’s capabilities.
- If you use Generative AI such as ChatGPT, please try to understand what ChatGPT gives you.
- Copying and pasting it without any understanding harms your learning opportunity.
DANL Tools
What is Git?

\(\quad\)
- Git is the most popular version control tool for any software development.
- It tracks changes in a series of snapshots of the project, allowing developers to revert to previous versions, compare changes, and merge different versions.
- It is the industry standard and ubiquitous for coding collaboration.
What is GitHub?
GitHub is a web-based hosting platform for Git repositories to store, manage, and share code.
Out class website is hosted on a GitHub repository.
Course contents will be posted not only in Brightspace but also in our GitHub repositories (“repos”) and websites.
Github is useful for many reasons, but the main reason is how user friendly it makes uploading and sharing code.
What is GitHub?
What is Python?
Python is a versatile programming language known for its simplicity and readability.
Python has become a dominant tool in various fields including data analysis, machine learning, and web development.
- It is widely used among developers, data scientists, and researchers for building applications and performing data-driven tasks.
- Python is open source and has a vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks.
What is Jupyter?
- Jupyter is an open-source integrated development environment (IDE) primarily for Python, though it supports many other languages.
- An IDE is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities (e.g., text code editor, graphical user interface (GUI)) to users for a programming-related project.
- Jupyter provides a notebook interface that allows users to write and execute code in a more interactive and visual format.
What is Jupyter Notebook?
- Jupyter Notebook (
*.ipynb) is a user-friendly environment that enhances coding, data analysis, and visualization.- It offers a web-based interface that combines live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text.
- Jupyter Notebook is widely used for data science, machine learning, and research, enabling easy sharing and collaboration.
- We will use Google Colab, a free cloud version of Jupyter.
What is RStudio?
RStudio is an IDE mainly for R programming.
RStudio is a user-friendly interface that makes using R easier and more interactive.
- It provides a console, syntax-highlighting editor that supports direct code execution, as well as tools for plotting, history, debugging, and workspace management.
We will use RStudio to manage a personal website, where HTML files are rendered from Quarto Document and Jupyter Notebook.
Installing the Tools
Installing the Tools
R programming
- The R language is available as a free download from the R Project website at:
- Windows: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/
- Mac: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/macosx/
- Download the file of R that corresponds to your Mac OS (Big Sur, Apple silicon arm64, High Sierra, El Capitan, Mavericks, etc.)
Installing the Tools
R Studio
- The RStudio Desktop is available as a free download from the following webpage:
- For Mac users, try the following steps:
- Run
RStudio-*.dmgfile. - From the Pop-up menu, click the RStudio icon.
- While clicking the RStudio icon, drag it to the Applications directory.
- Run
Installing the Tools
RStudio Environment
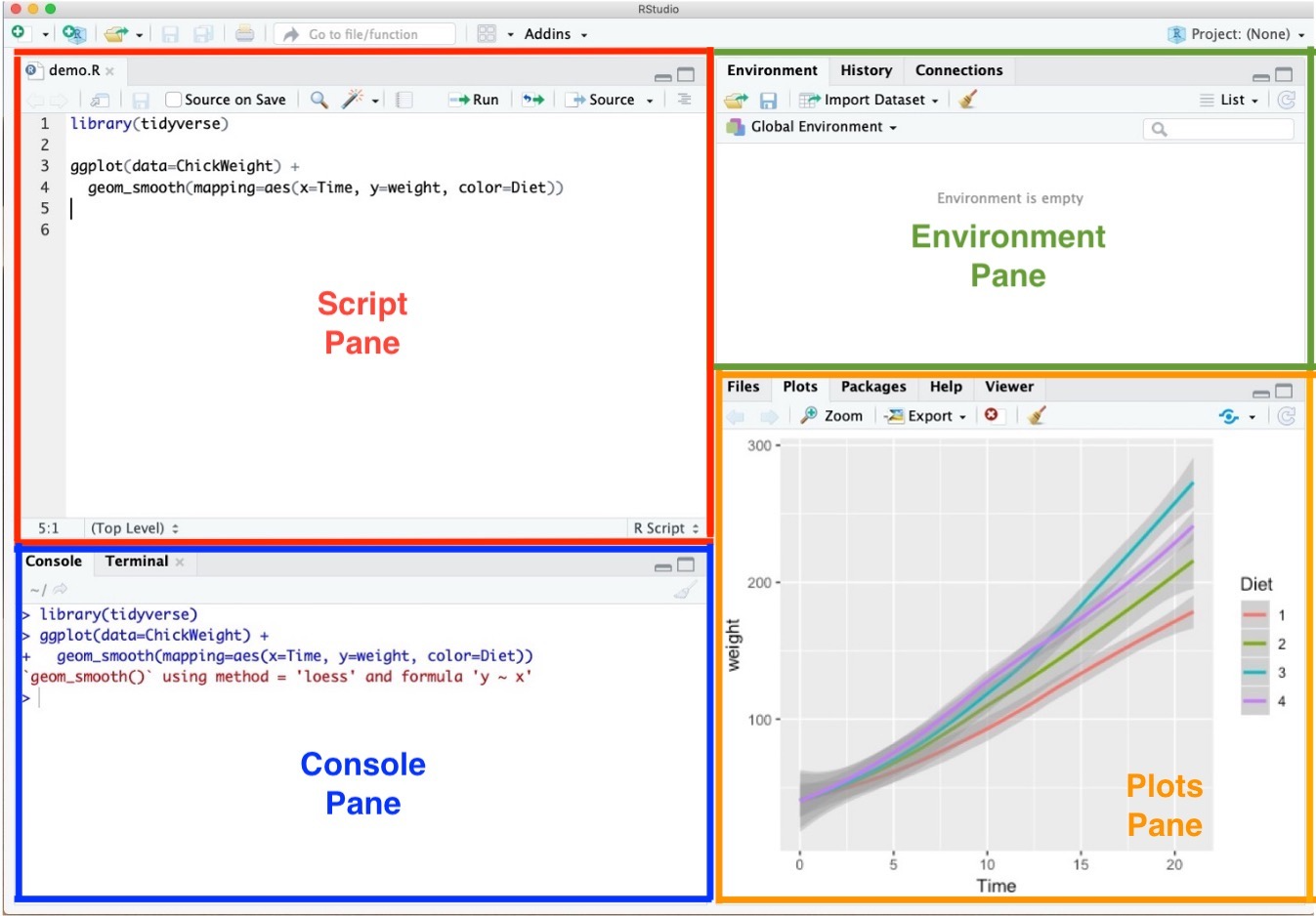
Script Pane is where you write R commands in a script file that you can save.
- An R script is simply a text file containing R commands.
- RStudio will color-code different elements of your code to make it easier to read.
- To open an R script,
- File \(>\) New File \(>\) R Script
- To save the R script,
- File \(>\) Save
Installing the Tools
RStudio Environment

- Console Pane allows you to interact directly with the R interpreter and type commands where R will immediately execute them.
Installing the Tools
RStudio Environment
Installing the Tools
RStudio Environment

- Plots Pane contains any graphics that you generate from your R code.
Installing the Tools
R Packages and tidyverse
- R packages are collections of R functions, compiled code, and data that are combined in a structured format.
- The
tidyverseis a collection of R packages designed for data science that share an underlying design philosophy, grammar, and data structures.- The
tidyversepackages work harmoniously together to make data manipulation, exploration, and visualization more. - We will use several R packages from
tidyversethroughout the course. (e.g.,ggplot2,dplyr,tidyr)
- The
Installing the Tools
Installing R packages with install.packages("packageName")
- R packages can be easily installed from within R using functions
install.packages("packageName").- To install the R package
tidyverse, type and run the following from R console:
- To install the R package
- While running the above codes, you may encounter the question below from the R Console:
- Mac: “Do you want to install from sources the packages which need compilation?” from Console Pane.
- Windows: “Would you like to use a personal library instead?” from Pop-up message.
- Type
noin the R Console, and then hit Enter.
Installing the Tools
Loading R packages with library(packageName)
- Once installed, a package is loaded into an R session using
library(packageName)so that its functions and data can be used.- To load the R package
tidyverse, type and run the following command from a R script:
- To load the R package
mpgis the data.frame provided by the R packageggplot2, one of the R pakcages intidyverse.
Installing the Tools
RStudio Options Setting
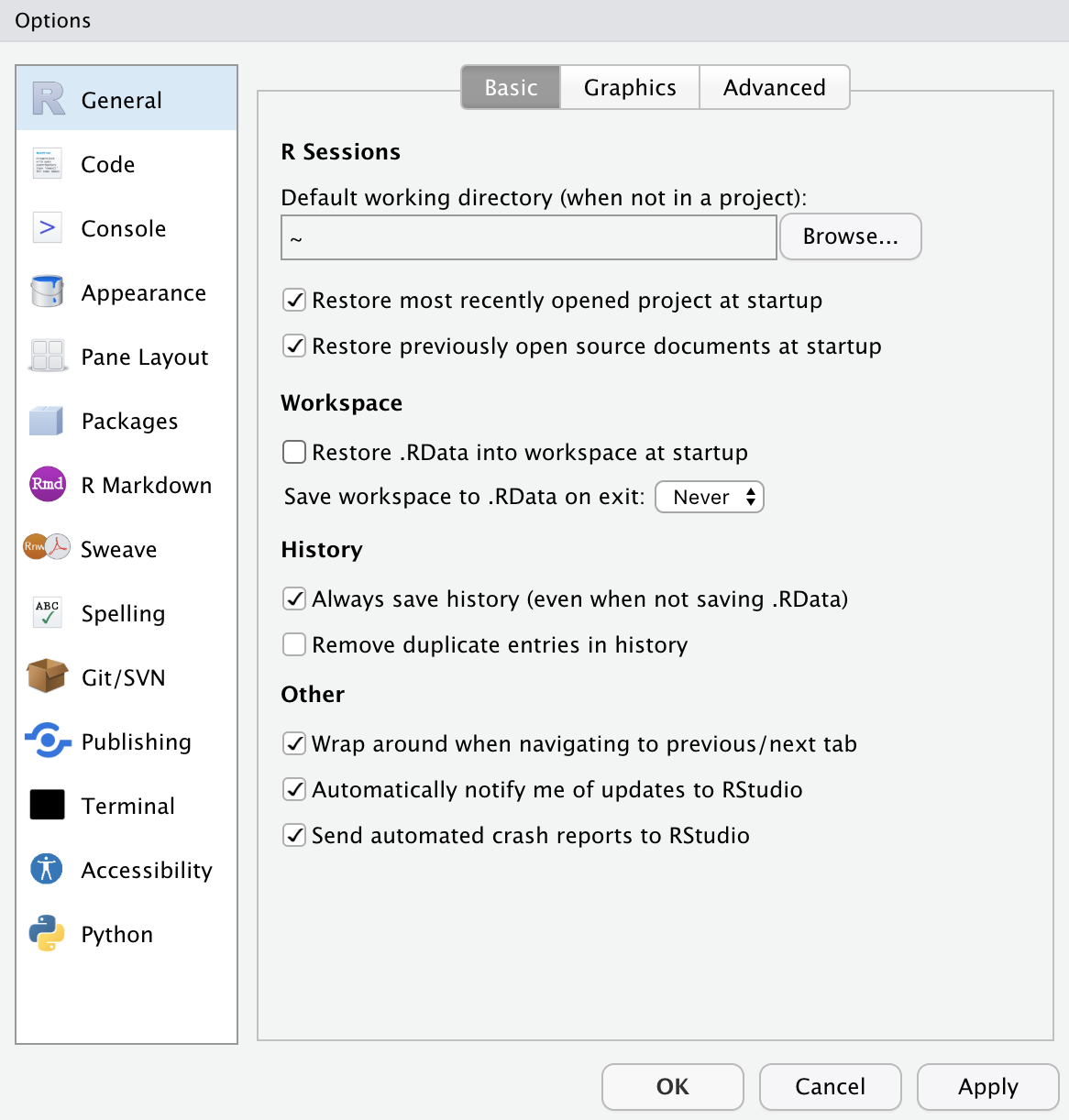
- This option menu is found by menus as follows:
- Tools \(>\) Global Options
- Check the boxes as in the left.
- Choose the option Never for Save workspace to .RData on exit:
Installing the Tools
Anaconda
- To install Anaconda, go to the following download page:
- https://www.anaconda.com/products/distribution.
- Click the “Download” button.
- To work on web-scrapping and APIs, we will use Spyder IDE provided by Anaconda.
Building a Personal Website on GitHub
- Follow steps described in Classwork 1.
Let’s Practice Markdown!
Jupyter Notebook, Quarto, and GitHub-based Discussion Boards use markdown as its underlying document syntax.
Let’s do Classwork 2.